Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research details a novel approach to building more resilient stablecoin systems using collaborative, trust-weighted data aggregation.
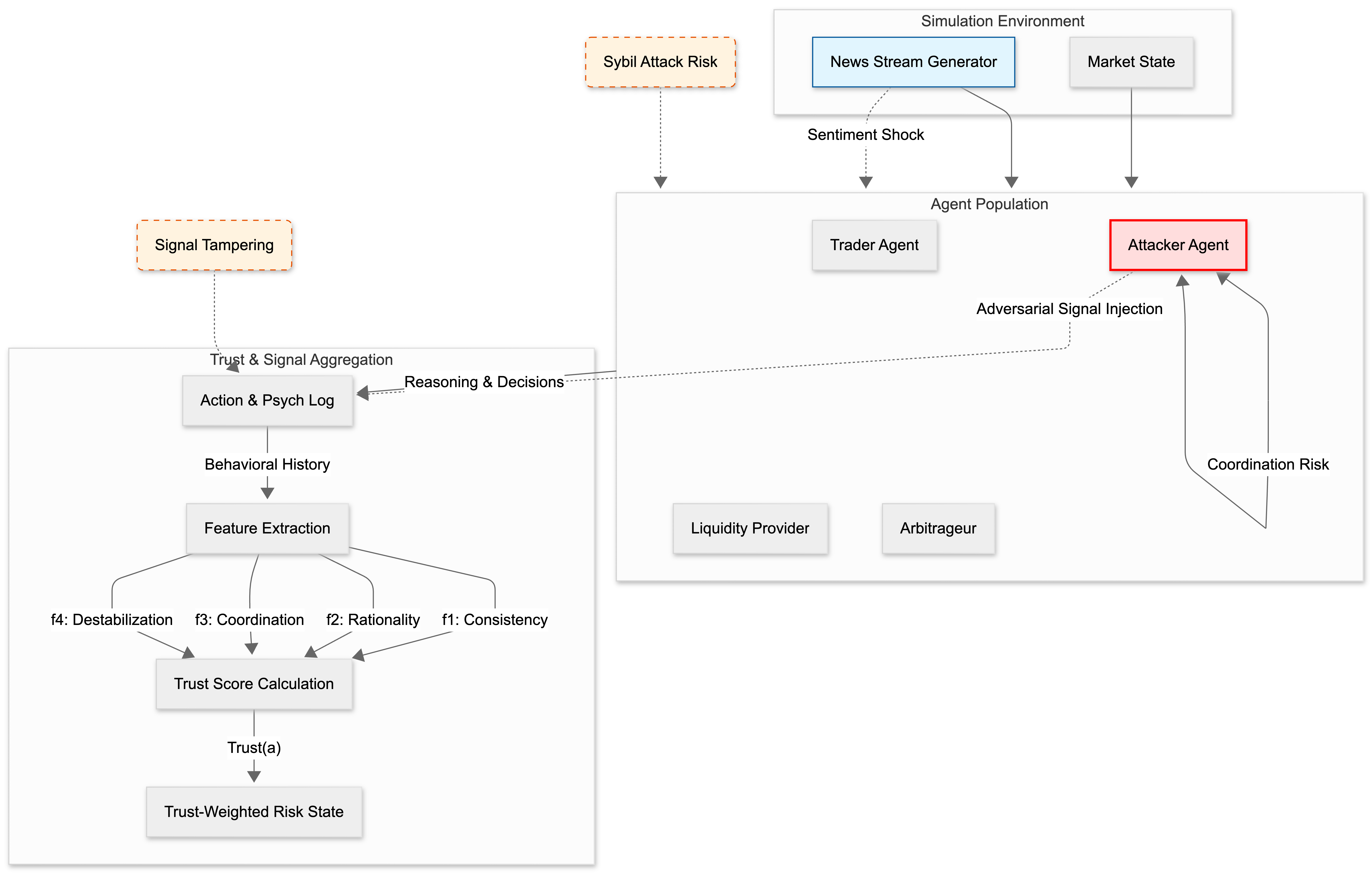
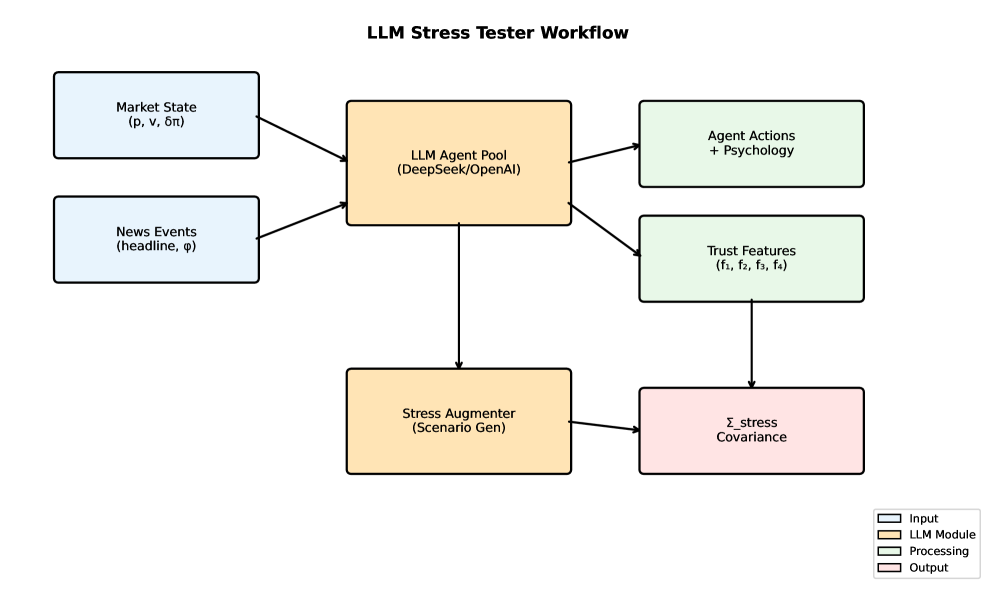
This paper introduces a trust-weighted signal aggregation mechanism for multi-agent systems to improve stablecoin reserve management robustness against adversarial attacks and enhance distributed system security.
Existing algorithmic stablecoin designs struggle to maintain stability under extreme market stress due to reliance on historical data that fails to capture tail events. This paper, ‘Stablecoin Design with Adversarial-Robust Multi-Agent Systems via Trust-Weighted Signal Aggregation’, introduces MVF-Composer, a novel reserve controller leveraging multi-agent simulations and a trust-weighted signal aggregation mechanism to enhance robustness against adversarial attacks. By simulating crisis scenarios and down-weighting signals from manipulative agents, MVF-Composer reduces peak peg deviation by 57% compared to existing systems. Can this approach to stress-testing and trust-based signal filtering be generalized to improve the resilience of other decentralized finance protocols and distributed systems?
The Illusion of Control: Systemic Risk in Complex Networks
Contemporary technological infrastructure is characterized by a growing dependence on multi-agent systems – networks comprising numerous interacting entities, from software bots and autonomous vehicles to financial trading algorithms and smart grid components. This increasing complexity, while enabling remarkable functionality and efficiency, simultaneously introduces novel and often subtle vulnerabilities. Each agent, even if individually secure, contributes to a systemic risk profile as interactions amplify the potential for cascading failures or coordinated attacks. A disruption affecting a small number of agents can propagate rapidly throughout the entire system, leading to unforeseen consequences and potentially widespread damage, as the aggregate behavior of these interconnected components becomes difficult to predict or control. The sheer scale and dynamic nature of these systems challenge traditional security paradigms, necessitating a shift towards proactive risk assessment and the development of resilient architectures.
Conventional security paradigms, designed to address isolated threats, often falter when confronted with the intricacies of multi-agent systems. These systems, characterized by decentralized control and emergent behavior, present a shifting attack surface that traditional perimeter-based defenses cannot effectively contain. The challenge lies not merely in identifying individual malicious actors, but in detecting coordinated attacks where subtle manipulations of numerous agents combine to produce systemic failures. A single compromised agent may appear innocuous in isolation, yet, when operating in concert with others, can trigger cascading effects, overwhelming safeguards and disrupting the entire network. Consequently, security assessments must move beyond reactive measures and embrace proactive strategies capable of modeling complex interactions and anticipating emergent vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
The increasing sophistication of multi-agent systems necessitates a fundamental shift from reactive security measures to proactive defenses. Exploitable vulnerabilities aren’t limited to individual agents; malicious actors can orchestrate coordinated attacks that leverage the complex interactions within the system, causing cascading failures or subtle manipulations difficult to detect. Robust defense mechanisms must therefore move beyond perimeter security and focus on systemic risk – anticipating potential attack vectors, modeling the propagation of malicious influence, and developing resilient architectures capable of withstanding coordinated disruption. This requires not only advanced threat detection but also the implementation of adaptive control strategies and the capacity for self-healing, ensuring continued operation even under adverse conditions and safeguarding the integrity of the entire system against evolving threats.
Mirroring Intent: Behavioral Analysis for Agent Identification
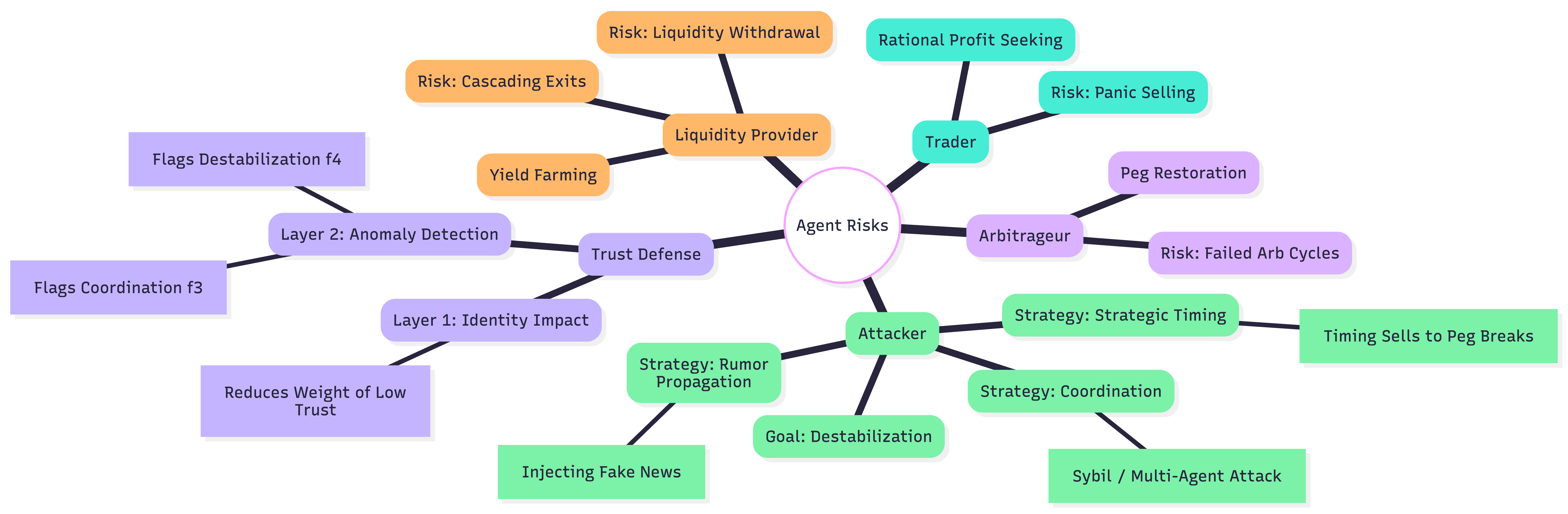
The TrustScoringMechanism operates by continuously evaluating the consistency of an agent’s actions within the system. This analysis doesn’t require prior knowledge of the agent’s identity or established reputation; instead, it focuses solely on the correlation between stated sentiments and subsequent actions. Each action is weighted based on its potential impact on the system, and deviations from expected behavior, given the agent’s expressed sentiment, contribute to a decreasing trust score. The mechanism utilizes a dynamic threshold; consistently rational behavior maintains a high score, while inconsistent or destabilizing actions lower the score, flagging potentially adversarial agents for further review or mitigation. This approach allows for the identification of malicious actors even when they employ new or previously unseen strategies.
The TrustScoringMechanism operates independently of pre-existing agent identities and historical reputation data. This design choice is critical for mitigating Sybil attacks, where a malicious entity creates multiple pseudonymous identities to exert disproportionate influence. Traditional reputation systems are inherently vulnerable to these attacks because newly created, but ostensibly reputable, identities can rapidly accumulate influence. By focusing solely on real-time behavioral analysis, the mechanism assesses each action in isolation, without reference to any prior history or assumed identity. This approach effectively neutralizes the advantage gained by attackers leveraging multiple identities, as each identity is evaluated solely on its current behavior, preventing the artificial inflation of trust scores based on coordinated activity across multiple accounts.
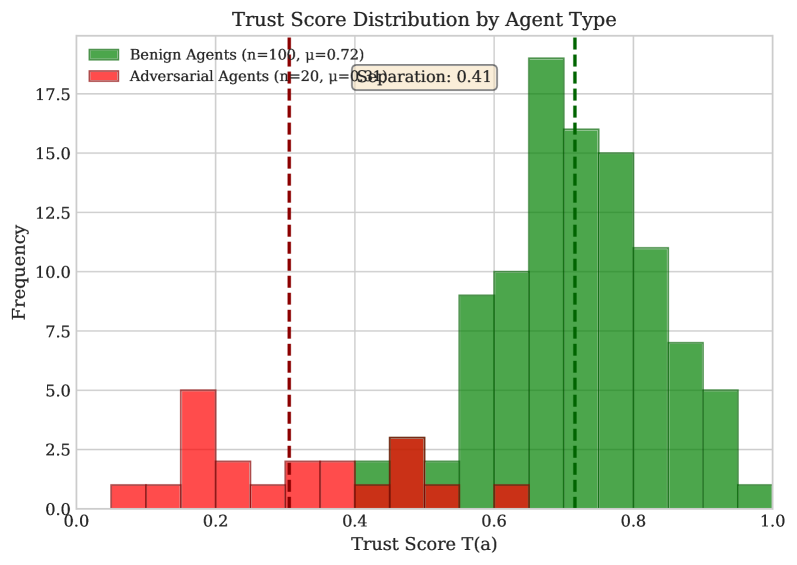
The identification of malicious agents relies on evaluating SentimentActionConsistency and detecting DestabilizationPatterns within agent behavior. SentimentActionConsistency measures the alignment between expressed sentiment and corresponding actions; rational actors generally exhibit a positive correlation, while adversarial agents may demonstrate incongruent behavior. DestabilizationPatterns refer to actions specifically designed to disrupt system equilibrium, such as disproportionate negative contributions or attempts to manipulate consensus mechanisms. Through the combined analysis of these factors, the TrustScoringMechanism effectively differentiates between constructive and destructive participants, resulting in a measured 49% reduction in Sybil attack influence based on testing data.
The Weight of Belief: Intelligent Signal Aggregation and Resource Allocation
SignalAggregation and TrustWeightedAggregation are employed to consolidate data received from multiple agents within the system. SignalAggregation combines these inputs into a unified intelligence stream, while TrustWeightedAggregation refines this process by assigning variable weights to each agent’s contribution. These weights are determined by an established trust score, reflecting the historical reliability and accuracy of each agent’s data. This prioritization of trustworthy sources ensures that more credible information exerts a greater influence on overall system intelligence, improving the quality of aggregated data used for downstream decision-making processes.
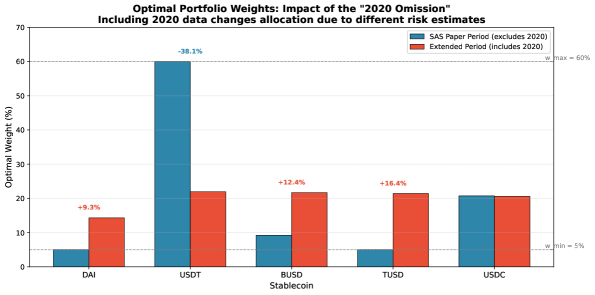
The aggregated intelligence derived from signal and trust-weighted signal aggregation is integrated into a Mean-Variance Optimization (MVO) framework to determine optimal allocations for the StablecoinReserve. MVO, a portfolio optimization technique, calculates the expected return and volatility for various asset allocations, aiming to maximize returns for a given level of risk, or conversely, minimize risk for a target return. Within this system, the aggregated signals function as inputs defining expected asset performance, while the framework’s calculations identify the portfolio weights – the proportion of the StablecoinReserve allocated to each asset – that best satisfy the specified optimization criteria. This process allows for dynamic and data-driven resource allocation, adapting to changing market conditions and risk profiles as indicated by the aggregated intelligence.
The system’s trust-weighted signal aggregation mechanism demonstrably reduces the impact of malicious actors on stablecoin reserve control. Testing indicates a 60-80% reduction in adversarial influence, achieved by prioritizing signals from highly trusted agents and down-weighting those from sources with lower trustworthiness scores. This directly correlates to a 57% decrease in the success rate of attacks targeting the stablecoin reserve, resulting in enhanced system resilience and a mitigation of potential financial losses. The mechanism operates by assigning weights to incoming signals based on a dynamic trust assessment, effectively minimizing the ability of compromised or malicious agents to manipulate resource allocation decisions.
The Illusion of Control: Stress-Testing Resilience with Simulated Adversaries
A novel multi-agent simulation environment, termed StressHarness, is employed to proactively generate realistic and challenging adversarial scenarios. This system moves beyond reactive security testing by constructing potential future attacks, allowing for the pre-emptive evaluation of system resilience. Rather than relying on known attack patterns, StressHarness dynamically creates complex situations involving numerous interacting agents, each with defined goals and capabilities. The environment enables researchers to explore a wider range of threats, including zero-day exploits and sophisticated, coordinated attacks, ultimately strengthening defenses by identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited in the real world. This forward-looking approach offers a critical advantage in the ongoing cybersecurity arms race, allowing systems to evolve and adapt to emerging threats.
The StressHarness achieves a new level of realism through the integration of large language models (LLMs), enabling the creation of autonomous agents capable of exhibiting complex and adaptive behaviors. Unlike traditional simulations relying on pre-programmed responses, these LLM-driven agents can dynamically formulate and execute sophisticated attack strategies, mirroring the tactics employed by real-world adversaries. This capability extends beyond simple mimicry; agents can learn from interactions within the simulated environment, refine their approaches, and even coordinate with one another to maximize impact. By leveraging the generative power of LLMs, the StressHarness moves beyond predictable scenarios, creating a continuously evolving threat landscape for robust resilience testing and the development of proactive defense mechanisms.
Within the StressHarness simulation, discerning coordinated attacks requires specialized techniques; the system employs CoordinationDetection to pinpoint malicious activity stemming from multiple agents acting in concert. This isn’t simply about identifying numerous attacks, but recognizing patterns indicative of a unified strategy. Recovery time, a critical metric for evaluating system resilience, is mathematically modeled as T_{rec} = 1/γ * ln(δ_s/ϵ), where γ represents the system’s inherent responsiveness, δ_s signifies the scale of the successful attack, and ϵ denotes the acceptable level of residual risk. This formula allows for predictive analysis of recovery duration based on attack characteristics and system parameters, providing valuable insights into bolstering defenses and minimizing downtime in the face of sophisticated, coordinated threats.
The presented research rigorously addresses the vulnerabilities inherent in distributed systems, particularly concerning stablecoin reserve management. The development of a trust-weighted signal aggregation mechanism represents a significant step towards achieving Byzantine fault tolerance, mitigating the impact of adversarial attacks that seek to disrupt systemic stability. This approach acknowledges that no single agent possesses complete information, and that reliance on aggregated, yet critically assessed, signals is paramount. As Carl Sagan observed, “Somewhere, something incredible is waiting to be known.” This sentiment encapsulates the core pursuit of the study-to unveil and address the hidden vulnerabilities within complex systems, striving for a more robust and secure future for decentralized finance. The curvature metrics of trust assignment, while complex, represent a sophisticated attempt to navigate the inherent uncertainties within a multi-agent environment.
What Lies Beyond the Horizon?
The pursuit of robust stablecoin designs, as illustrated by this work on trust-weighted signal aggregation, reveals a fundamental tension. Any system built upon the premise of distributed consensus – a multi-agent system striving for a singular value – inevitably confronts the specter of imperfection. The elegance of Byzantine fault tolerance, of weighting signals based on perceived trust, is not a solution, but a postponement. It shifts the locus of vulnerability, trading one set of assumptions for another. The model simplification inherent in any such formalization requires strict mathematical rigor, yet even the most meticulously crafted equations are but approximations of a chaotic reality.
Future investigations should not focus solely on refining the mechanisms of trust assignment. A more profound inquiry concerns the very definition of ‘truth’ within a distributed network. Can a system truly be secure if its constituent agents operate under differing, potentially conflicting, interpretations of value? The concept of ‘adversarial attacks’ presupposes an external malevolence, but the most insidious failures may arise from internal inconsistencies, from the subtle erosion of shared understanding.
Ultimately, the quest for a perfect stablecoin, or indeed any perfectly robust system, may be a delusion. Like attempting to map the singularity within a black hole, the very act of observation introduces distortion. The horizon remains, not as a barrier to be overcome, but as a reminder of the limits of knowledge and control.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.22168.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Lacari banned on Twitch & Kick after accidentally showing explicit files on notepad
- YouTuber streams himself 24/7 in total isolation for an entire year
- Adolescence’s Co-Creator Is Making A Lord Of The Flies Show. Everything We Know About The Book-To-Screen Adaptation
- Gold Rate Forecast
- The Batman 2 Villain Update Backs Up DC Movie Rumor
- 2026 Upcoming Games Release Schedule
- Answer to “A Swiss tradition that bubbles and melts” in Cookie Jam. Let’s solve this riddle!
- Now you can get Bobcat blueprint in ARC Raiders easily. Here’s what you have to do
- PUBG Creator Says He Is “Really heartened” About The Backlash To AI In Gaming
- Save Up To 44% on Displate Metal Posters For A Limited Time
2026-02-02 08:12