Eyes on the Earth: Documenting Resource Extraction with AI
A new system uses artificial intelligence to analyze satellite imagery of mining sites worldwide, creating a lasting record of environmental impact.
A new system uses artificial intelligence to analyze satellite imagery of mining sites worldwide, creating a lasting record of environmental impact.
New research explores the growing psychological risks and dependencies associated with using AI chatbots, drawing insights from real user experiences.
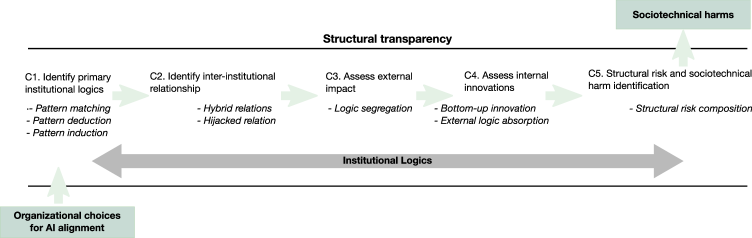
New research reveals that understanding the decision-making processes within organizations is crucial to building AI systems that reflect human values.
A new framework reveals the hidden vulnerabilities in AI voice agents, highlighting the need for robust defenses against increasingly sophisticated attacks.
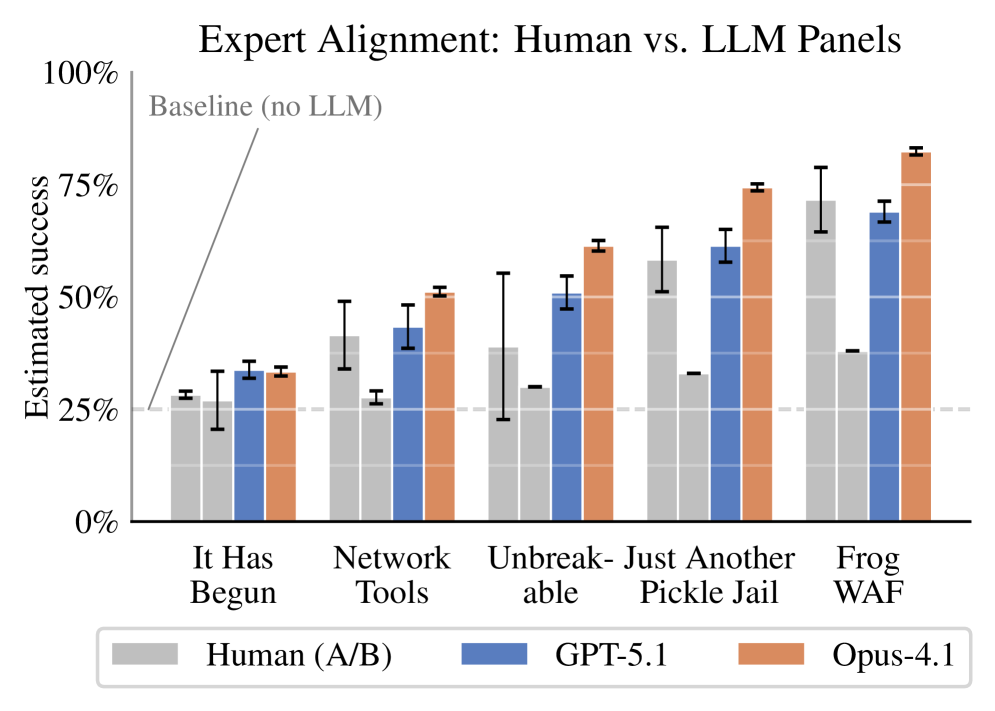
New research shows artificial intelligence can effectively scale expert judgment for evaluating complex threats, particularly in cybersecurity.
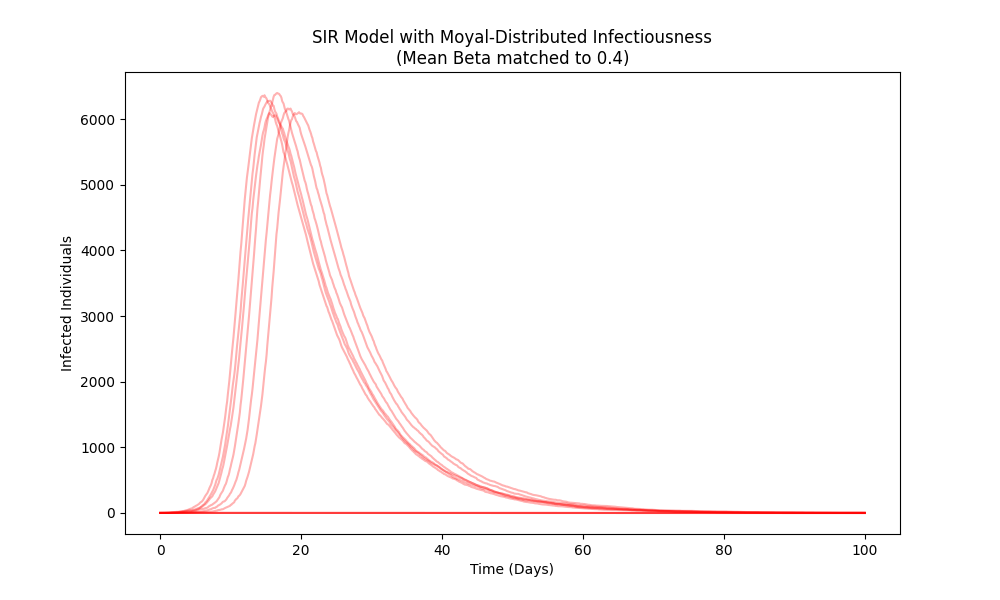
A new theoretical framework leverages the Moyal distribution to connect microscopic transmission events with the large-scale patterns observed in pandemic outbreaks.
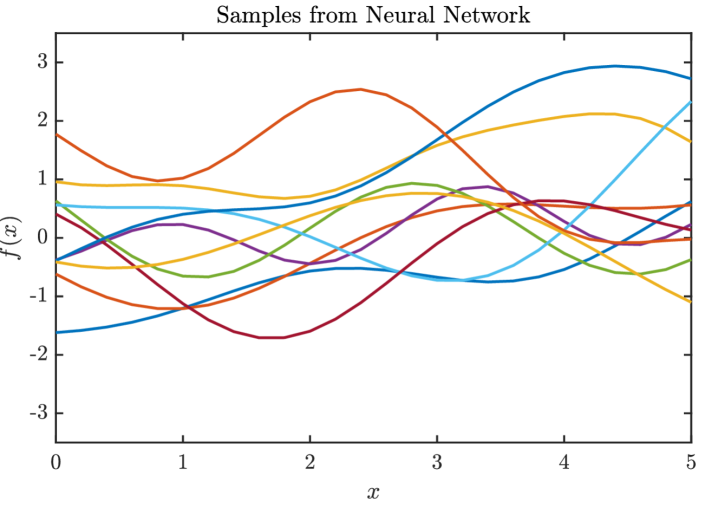
New research reveals a surprising mathematical link between the established field of spatial statistics and the rapidly evolving world of large neural networks.
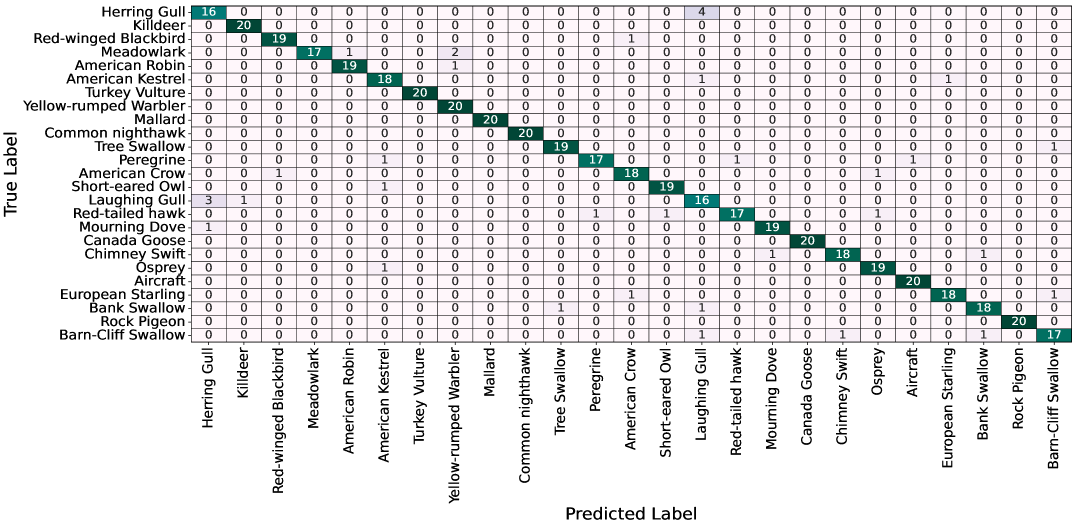
New research explores how deep learning can improve bird strike prevention by automatically identifying species and predicting flock behavior near airports.
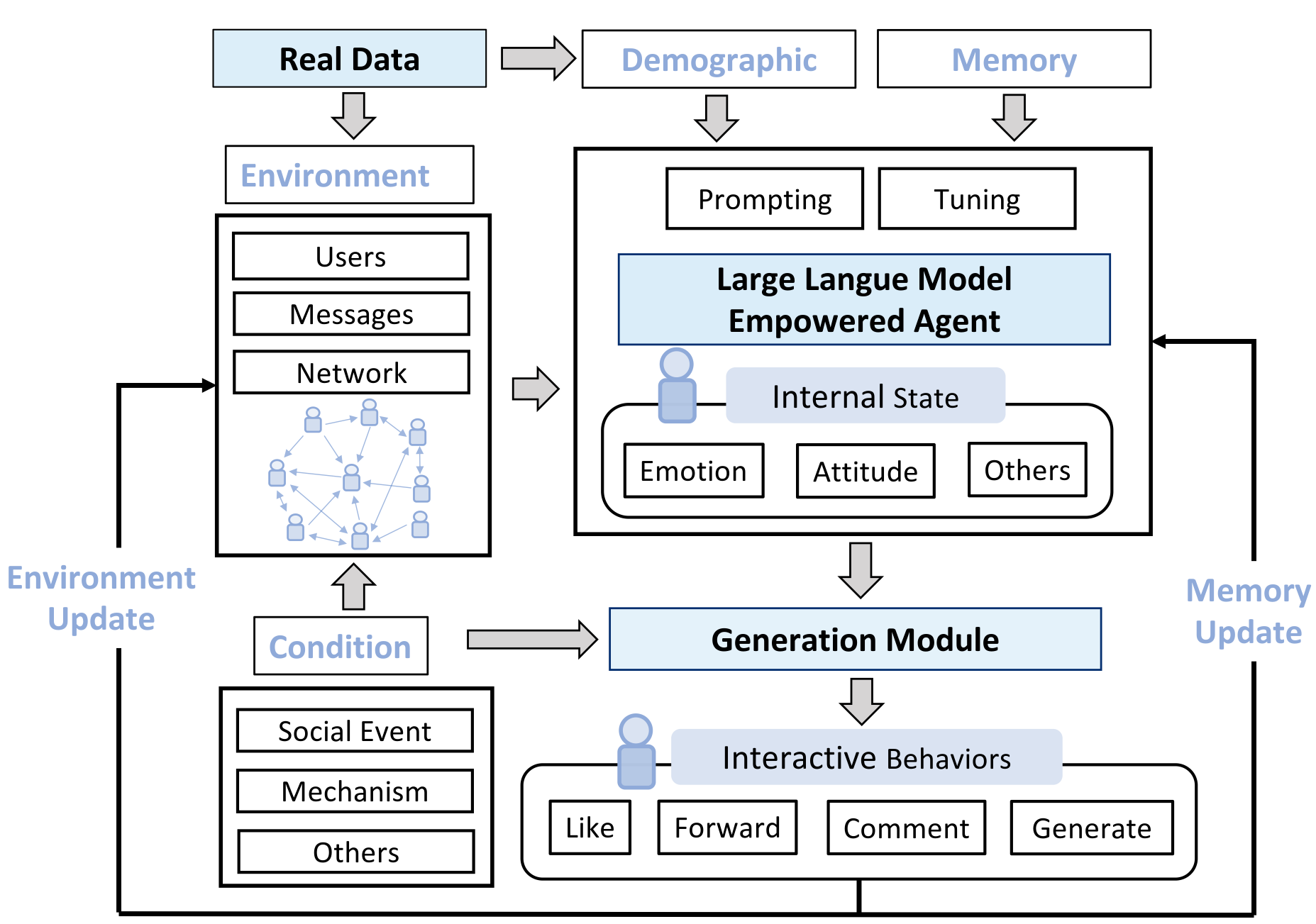
New research explores how large language models are being leveraged to understand and predict the dynamics of spreading processes, from disease outbreaks to the viral spread of information.

New research demonstrates how learned representations of bond characteristics can dramatically improve similarity searches and modeling in fixed-income markets.