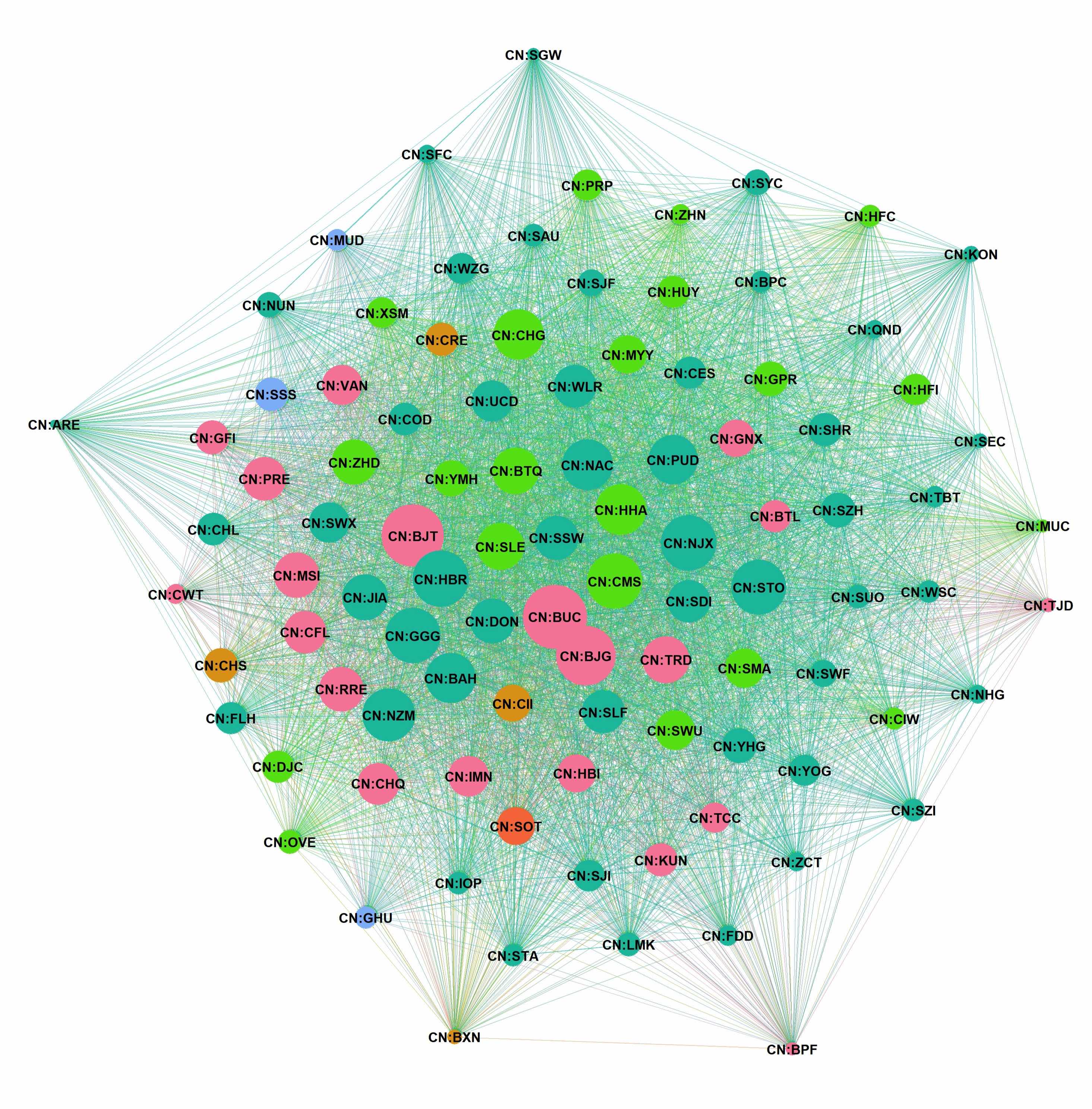
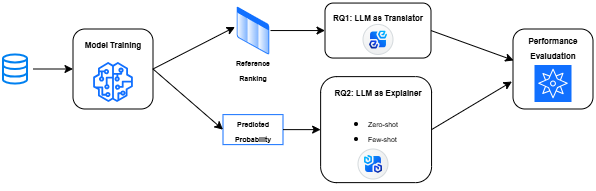
The Echo in the Machine: How Generative Models Find Their Rhythm
![The study demonstrates a unifying framework for iterative feedback processes, revealing that diverse approaches - from acoustic experiments to advanced generative models like CycleGAN and diffusion models - collectively exhibit the dynamics of a Markov process, where successive model generations are linked by a transformation operator [latex]T(\cdot)[/latex] acting on the current image distribution [latex]X_n[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.19033v1/x19.png)
New research reveals that iterative feedback loops in image generation create a resonant state, explaining why these models sometimes get stuck and offering clues to unlock their full potential.