Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research reveals that standard power grid security assessments often fail to account for how actual market behavior impacts system resilience.
This review benchmarks a day-ahead market model for power systems and highlights the implications of realistic dispatch scenarios on security margins and cascading failure risk.
Traditional power system security assessments often rely on idealized operational scenarios, potentially overlooking the impact of realistic market dynamics. This research, detailed in ‘A day-ahead market model for power systems: benchmarking and security implications’, introduces a market model with a social-welfare-based day-ahead market clearing mechanism to address this gap. Results demonstrate that market-based dispatch can lead to up to 80% higher unserved demand compared to optimal power flow, revealing a significant overestimation of system security. How can operators leverage these insights to improve reserve allocation and enhance long-term expansion planning strategies for a more resilient grid?
The Shifting Landscape of Power System Vulnerability
The growing integration of renewable energy sources, while crucial for decarbonization, fundamentally alters the operational landscape of power systems. Unlike traditional fossil fuel-based generation, sources like solar and wind are inherently intermittent and geographically dispersed. This variability introduces volatility into the grid, creating challenges for maintaining a consistent balance between electricity supply and demand. Successfully integrating these resources requires constant adjustments to compensate for fluctuations, demanding greater flexibility and responsiveness from the entire system. Without careful management, these fluctuations can propagate through the network, potentially leading to localized instabilities and, in extreme cases, widespread blackouts – a risk that is becoming increasingly prominent as reliance on renewables continues to expand.
Conventional power system analysis relies heavily on static modeling and predefined scenarios, proving increasingly inadequate for the volatile realities of modern grids. These methods often underestimate the probability of extreme events and fail to capture the complex interactions between renewable energy sources, fluctuating demand, and increasingly interconnected infrastructure. Consequently, assessments of system security are frequently overly optimistic, creating a false sense of reliability. This miscalibration leaves power systems susceptible to cascading failures – where a localized disturbance rapidly propagates across the network, triggering widespread outages – because critical vulnerabilities remain undetected during routine evaluations. The inability to accurately predict system behavior under stress highlights a critical gap in preparedness and underscores the need for more robust and dynamic risk assessment tools.
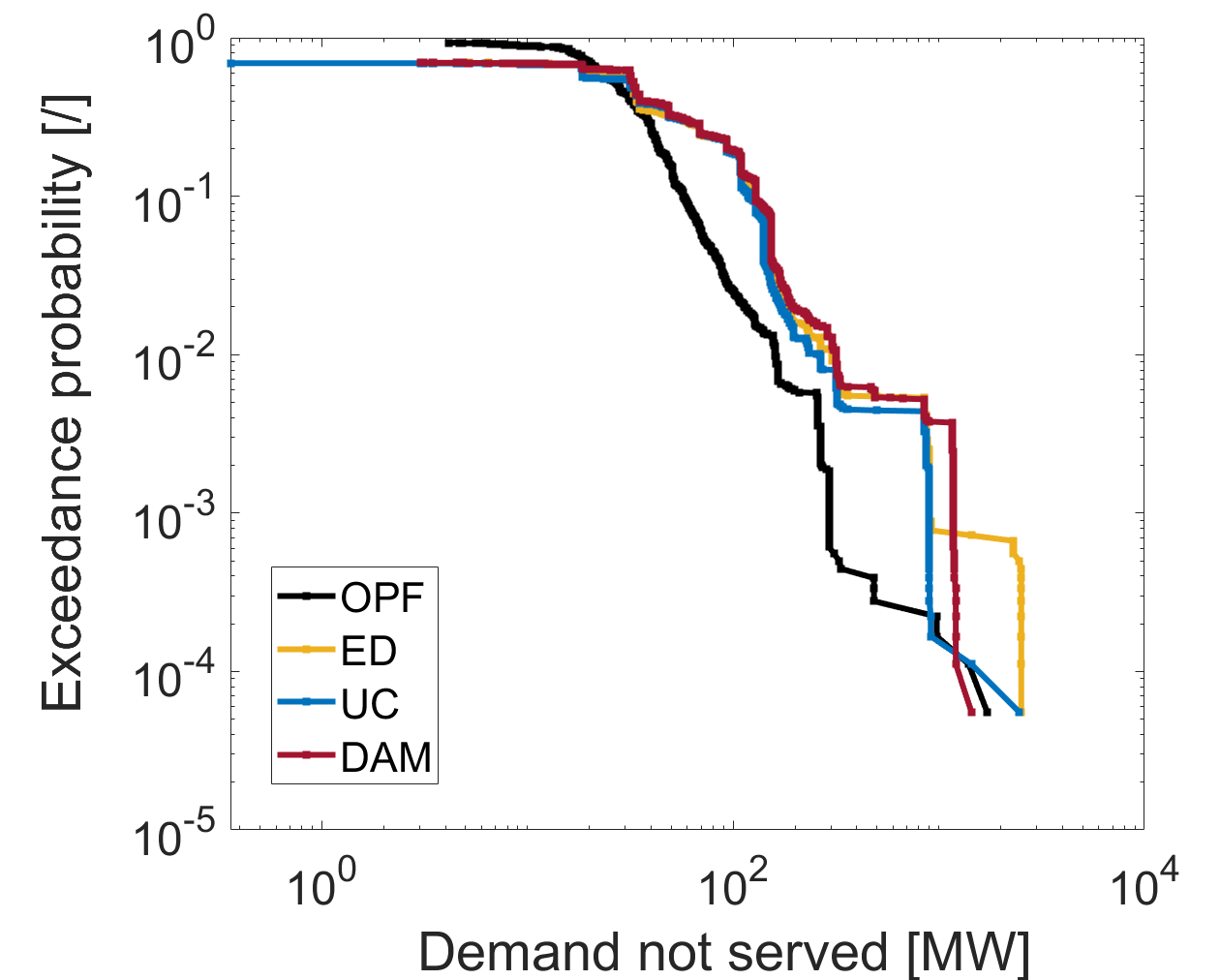
Contemporary power system modeling, while sophisticated, harbors critical limitations that increasingly jeopardize grid reliability. Existing analytical techniques frequently overestimate system security, creating a false sense of robustness as grids integrate more variable renewable energy sources. This overestimation stems from an inability to fully capture the complex, cascading effects of modern grid dynamics – a situation that could lead to a substantial 64% increase in unmet electricity demand under stressed conditions. Consequently, innovative modeling approaches are essential; these must move beyond traditional static assessments to incorporate real-time data, probabilistic forecasting, and advanced computational techniques capable of simulating a broader range of potential failure scenarios and ensuring a consistently supplied and stable power grid.
Modeling the Market: A Necessary Layer of Realism
The DayAheadMarketDispatch model functions as a simulation of economic interactions within the European power market, explicitly representing the behavior of generation companies motivated by profit maximization. This is achieved through unit commitment and economic dispatch calculations, where generators submit bids based on their marginal costs and are selected to meet demand at market-clearing prices. The model considers various constraints including generator capacity, ramp rates, and transmission network limitations. By simulating this competitive bidding process, the model generates a realistic representation of market outcomes, allowing for analysis of price formation, generator behavior, and the impact of different market designs or regulatory interventions. This approach contrasts with optimal power flow (OPF) based dispatch which often assumes cost minimization without explicitly modeling profit-driven strategies.
The DayAheadMarketDispatch model integrates two key components to simulate European power market behavior: LongTermPositionOptimization and the RedispatchModel. LongTermPositionOptimization accounts for the strategic bidding practices of market participants, allowing the model to capture how generators optimize their positions based on anticipated market conditions and competitor behavior. Simultaneously, the RedispatchModel addresses GridConstraints by simulating the corrective actions taken by system operators to alleviate congestion and maintain grid stability. This involves adjusting generation schedules and utilizing cross-border capacity to ensure power flows remain within acceptable limits, and is crucial for accurately representing the feasible operating space of the power system.
Analysis utilizing the DayAheadMarketDispatch model indicates that reliance on Optimal Power Flow (OPF)-based dispatch for assessing SystemSecurity can significantly overestimate grid stability. Results demonstrate a 64% increase in cumulative demand not served when comparing scenarios modeled with and without incorporating market-driven behavior. This discrepancy arises because OPF calculations do not inherently account for the profit-motivated bidding strategies of market participants, nor do they fully represent the effects of RedispatchModel interventions addressing GridConstraints. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation of system security requires modeling these market forces to accurately predict potential vulnerabilities and proactively mitigate risks to supply.
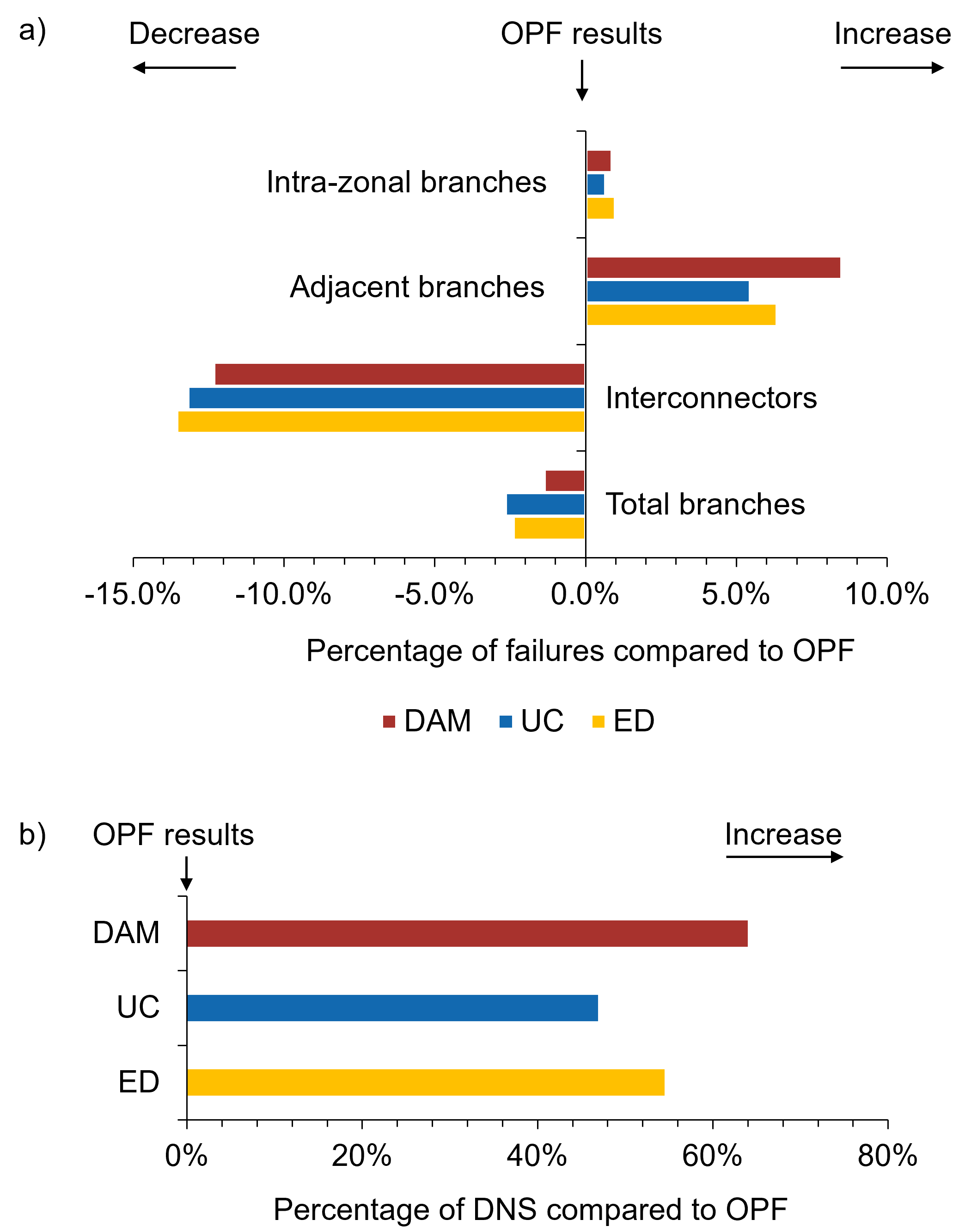
Dissecting Generation: From Cost Minimization to Operational Realism
Economic Dispatch (ED) functions as a foundational optimization method, determining the most cost-effective combination of available generation resources to meet demand. However, ED typically operates under simplified assumptions and doesn’t account for the operational characteristics of certain generation types. Unit Commitment (UC), conversely, expands upon ED by specifically optimizing the start/stop scheduling of ThermalGeneration assets and StorageUnits, which have associated costs and minimum uptime/downtime constraints. This scheduling process considers factors such as ramp rates, minimum operating levels, and startup/shutdown costs, resulting in a more realistic and potentially lower-cost generation plan than a purely cost-minimizing ED solution. While ED provides a baseline for comparison, UC is essential for accurately modeling the operational complexities of thermal and storage resources within a power system.
Optimal Power Flow (OPF) is an iterative process that refines resource allocation by directly incorporating GridConstraints – limitations imposed by the physical capacity and operational characteristics of the transmission network. Unlike EconomicDispatch and UnitCommitment which primarily focus on cost minimization, OPF simultaneously optimizes generation dispatch while ensuring adherence to line thermal limits, voltage bounds, and power flow regulations. This comprehensive approach allows for a more realistic assessment of system feasibility and provides a robust benchmark for evaluating the accuracy of other modeling techniques; deviations between OPF results and those from simplified models can highlight areas where model fidelity needs improvement to accurately represent grid behavior and potential operational constraints.
Analysis of generation scheduling methods reveals a direct relationship between resource allocation, grid limitations, and system stability. Specifically, implementation of the DayAheadMarketDispatch model yielded a reduction in redispatch costs of €326’124 when compared to combined results from Economic Dispatch and Unit Commitment approaches. This optimization, however, corresponded with a 21.9% increase in the highest recorded clearing price, reaching a peak of €248.8 €/MWh, indicating a trade-off between cost minimization and market pricing under the tested conditions.
Toward a More Resilient Grid: Reducing Dependence and Embracing Flexibility
The reliable delivery of electricity, whether generated from traditional thermal sources or increasingly prevalent renewable sources, is fundamentally constrained by the capacity of the existing transmission grid. Both ThermalGeneration and RenewableGeneration, despite differing operational characteristics, rely on TransmissionCapacity to move power from where it’s produced to where it’s consumed. This inherent dependence means that even substantial investments in new generation technologies will yield limited benefits without corresponding upgrades to grid infrastructure. Bottlenecks in transmission lines can curtail output from renewable energy facilities, leading to wasted potential, and can also limit the ability of thermal plants to respond to fluctuations in demand. Consequently, a robust and well-maintained transmission grid is not merely a supporting element of the power system, but a critical determinant of its overall efficiency, reliability, and ability to integrate diverse energy sources.
The integration of StorageUnits into power systems offers a potent strategy for diminishing reliance on expansive TransmissionCapacity, thereby bolstering overall system flexibility and reliability. These units, encompassing technologies like batteries and pumped hydro, function as buffers, absorbing excess energy during periods of high RenewableGeneration and releasing it when demand surges or renewable sources are unavailable. This localized energy management minimizes the strain on long-distance transmission lines, reducing congestion and potential cascading failures. Furthermore, strategically positioned StorageUnits can provide ancillary services – such as frequency regulation and voltage support – which are crucial for maintaining grid stability, particularly as the proportion of intermittent renewable energy sources increases. The result is a more responsive and robust power system, less vulnerable to disruptions and better equipped to handle the dynamic demands of a modern energy landscape.
Advanced power system modeling reveals opportunities to proactively enhance grid resilience and sustainability through refined market mechanisms. Simulations incorporating insights from storage unit deployment demonstrate that utilizing a DayAheadMarketDispatch model-as opposed to traditional Economic Dispatch-results in a substantial 4.3-fold increase in hours experiencing very high electricity prices-specifically, those exceeding 100 €/MWh. This finding suggests that while strategic dispatch can improve system flexibility, it also carries implications for price volatility and necessitates careful consideration of market design to balance reliability with affordability. By integrating these predictive capabilities into optimization algorithms, operators can anticipate potential stress points and implement preemptive strategies, ultimately fostering a more robust and economically viable power grid for the future.
The research highlights a critical vulnerability in conventional power system security assessments, revealing that idealized dispatch scenarios often paint an overly optimistic picture. This aligns with Karl Popper’s assertion that “The more we know, the more we realize how little we know.” The study demonstrates that neglecting realistic market behavior – specifically, the day-ahead market dynamics – can lead to a dangerous overestimation of system resilience, potentially masking the true risk of cascading failures. The findings underscore that progress in modeling complex systems necessitates continuous scrutiny and acknowledgment of inherent uncertainties, demanding a shift from seeking definitive answers to embracing a process of ongoing refinement and falsification.
What Lies Ahead?
The pursuit of increasingly accurate power system models reveals a recurring paradox: the more faithfully a simulation reflects market realities, the more apparent become the limitations of traditional security assessments. This work demonstrates that idealized dispatch scenarios, while computationally convenient, can create a dangerously optimistic illusion of system robustness. The algorithms used to allocate resources, it turns out, encode assumptions about rational actors and perfect information – assumptions that, when relaxed, reveal a landscape of cascading failures previously hidden beneath the veneer of optimization.
Future research must move beyond simply predicting system behavior and begin to explore the ethical implications of automating critical infrastructure. The drive towards greater algorithmic efficiency cannot be divorced from questions of equity, resilience, and accountability. Transparency is minimal morality, not optional. The field needs to consider not only if a system will fail, but who will bear the consequences when it does, and whether the optimization criteria themselves exacerbate existing vulnerabilities.
Ultimately, the challenge lies in recognizing that power systems are not merely engineering problems, but complex socio-technical systems. The algorithms used to manage them are not neutral tools, but active agents in shaping the future – creating the world through code, often unaware. A deeper understanding of the interplay between market dynamics, system security, and societal impact is therefore not simply a technical necessity, but a moral imperative.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.11842.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- United Airlines can now kick passengers off flights and ban them for not using headphones
- SHIB PREDICTION. SHIB cryptocurrency
- Movie Games responds to DDS creator’s claims with $1.2M fine, saying they aren’t valid
- Scream 7 Will Officially Bring Back 5 Major Actors from the First Movie
- These are the 25 best PlayStation 5 games
- The MCU’s Mandarin Twist, Explained
- Rob Reiner’s Son Officially Charged With First Degree Murder
- Server and login issues in Escape from Tarkov (EfT). Error 213, 418 or “there is no game with name eft” are common. Developers are working on the fix
- MNT PREDICTION. MNT cryptocurrency
- Gold Rate Forecast
2026-02-15 09:35