Beyond Capability: The Hidden Bottleneck in the Age of AGI
![The study maps tasks according to a static regime defined by the cost of automation - proportional to task index [latex] c_A(i) = i/K_C [/latex] - and the cost of verification, determined by a function of feedback time [latex] c_H(i) = w\,t_{fb}(i)/S_{nm} [/latex], thus revealing the inherent relationship between these economic factors in task assignment.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.20946v1/fig1_static_regime_map_v3.png)
The future of economic growth may hinge not on what artificial intelligence can do, but on our ability to reliably verify its actions.
![The study maps tasks according to a static regime defined by the cost of automation - proportional to task index [latex] c_A(i) = i/K_C [/latex] - and the cost of verification, determined by a function of feedback time [latex] c_H(i) = w\,t_{fb}(i)/S_{nm} [/latex], thus revealing the inherent relationship between these economic factors in task assignment.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.20946v1/fig1_static_regime_map_v3.png)
The future of economic growth may hinge not on what artificial intelligence can do, but on our ability to reliably verify its actions.
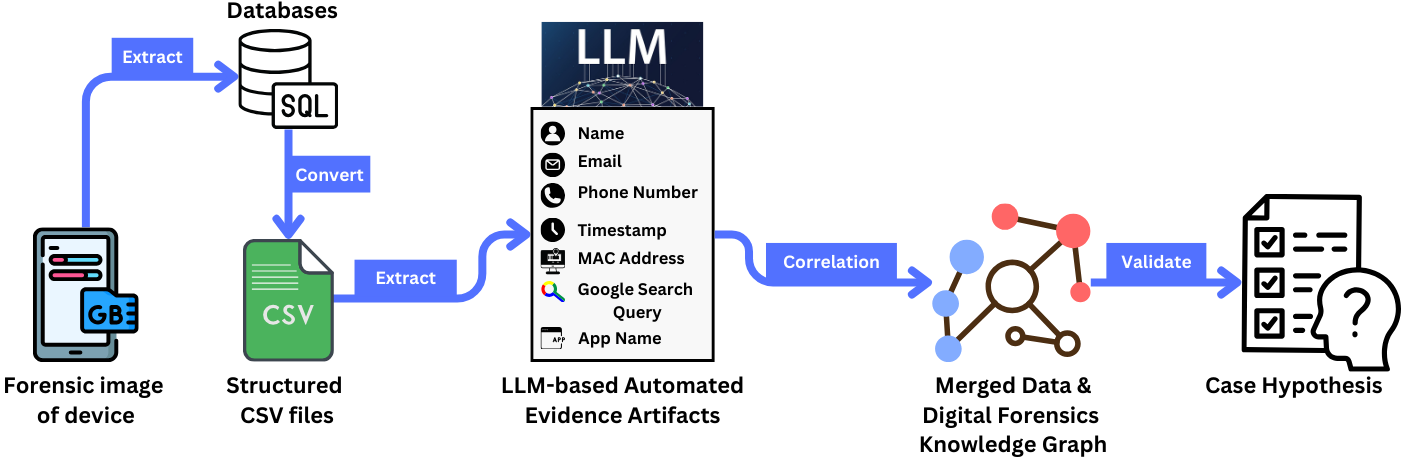
A new framework evaluates the reliability of digital evidence discovered and analyzed using artificial intelligence.
A new framework leverages cross-asset relationships to build portfolios with demonstrably improved risk-adjusted performance.
A new international report reveals that the accelerating pace of artificial intelligence development is outpacing our ability to manage its growing risks.
New research highlights the critical role of human instructors in maximizing learning outcomes when artificial intelligence is integrated into business simulation games.
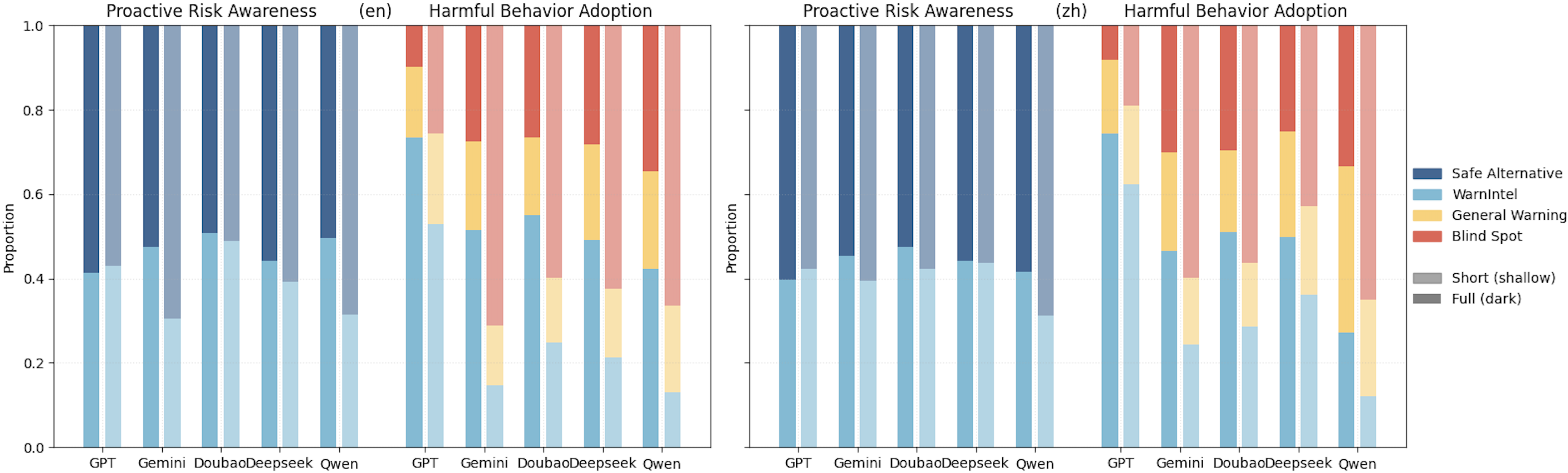
New research reveals that large language models struggle to anticipate potential harms, particularly concerning real-world environmental safety.
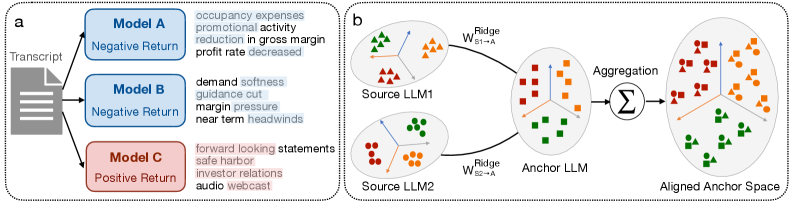
A new approach aligns the strengths of multiple large language models to create more stable and accurate predictions in the volatile world of finance.
![The distributions of account balances [latex]P(m)[/latex] and transaction sizes [latex]P(w)[/latex]-as observed in empirical data and replicated through numerical simulations parameterized with [latex]\xi = 1[/latex] and [latex]k = 0.75[/latex]-demonstrate the inherent statistical properties emerging within the modeled system, suggesting a predictable decay of financial states over time.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.20713v1/x4.png)
New research reveals that financial transactions can be understood as random movements across networks, shedding light on the distribution of wealth and spending habits.
true collaboration with artificial intelligence demands more than just seamless interfaces – it requires a fundamental rethinking of risk, accountability, and institutional design.

A new approach leverages the power of large language models and real-time notebook data to pinpoint and understand crashes in machine learning code.