Pricing Complexity: Tensor Networks Tackle Multi-Asset Options
A novel application of quantized tensor trains offers a scalable solution for accurately pricing options on multiple underlying assets, a longstanding challenge in computational finance.
A novel application of quantized tensor trains offers a scalable solution for accurately pricing options on multiple underlying assets, a longstanding challenge in computational finance.
A new stochastic model captures the erratic nature of trust, moving beyond traditional approaches to account for unpredictable jumps in decision-making.
Researchers have introduced a comprehensive dataset and evaluation framework to better assess the ability of artificial intelligence to understand and interpret financial credit information from both visual and textual sources.

New research reveals that the areas of dermoscopic images that AI algorithms prioritize directly impact their ability to accurately diagnose melanoma.
![The fitted spectral-NN estimator, parameterized with [latex]M=L=10[/latex], a depth of 4, a width of 20, and [latex]q=20[/latex], demonstrates a capacity for modeling complex relationships within three-dimensional fMRI data, yet its very structure-like any theoretical framework-risks being swallowed by the inherent limitations of its own design.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.00284v1/x1.png)
A new deep learning approach offers a computationally efficient way to analyze complex, high-dimensional time series data.
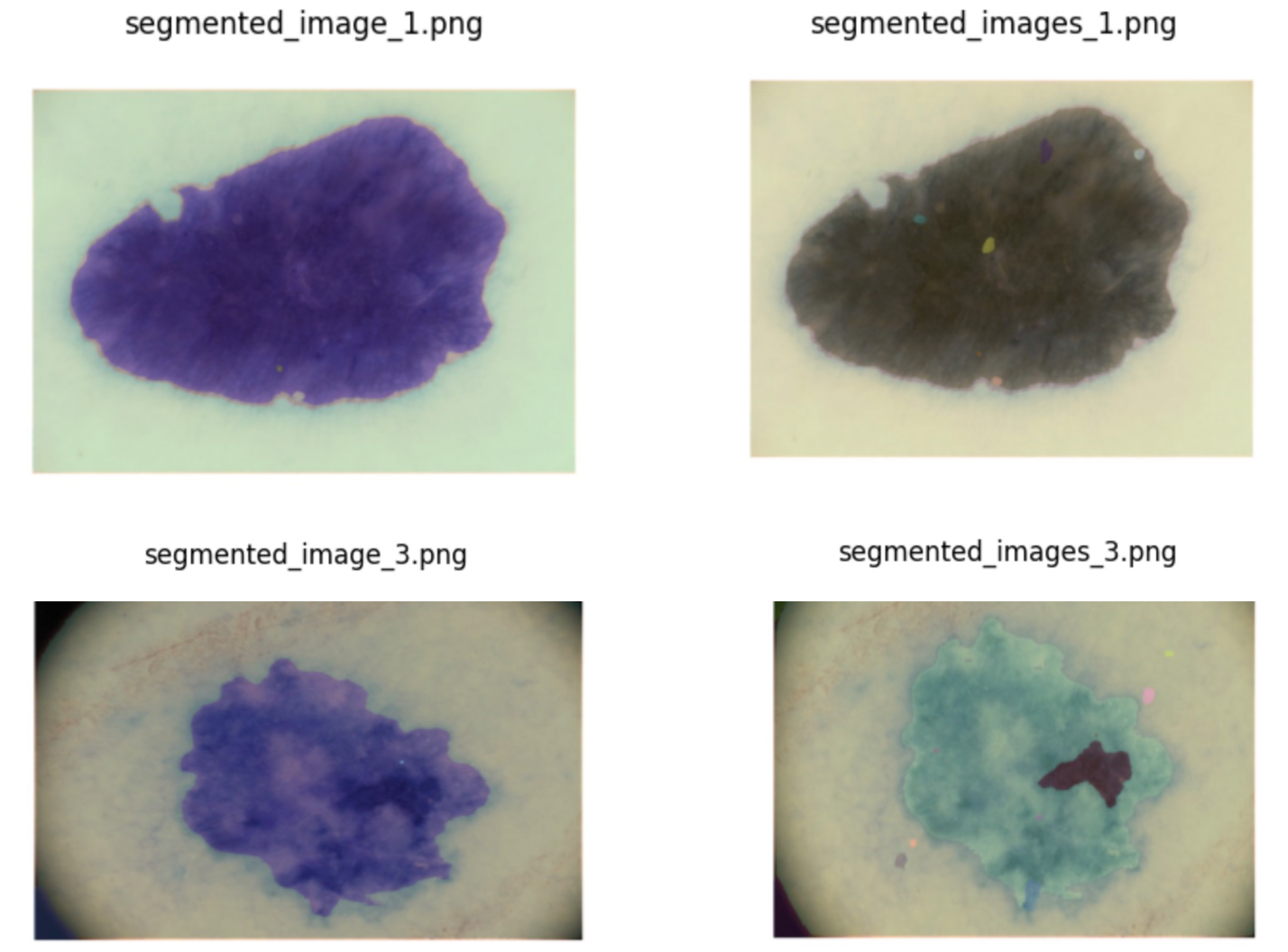
A new deep learning approach leveraging advanced neural networks is showing promising results in the automated and accurate identification of skin conditions.
New research demonstrates that incorporating non-traditional data sources-like climate risks and textual reports-can significantly enhance the accuracy of credit default predictions.

New research reveals consistent patterns of financial network reorganization during the pandemic, indicating heightened systemic risk and lingering vulnerabilities across global economies.

A new review challenges the assumption that artificial intelligence automatically improves regional climate projections, suggesting established methods remain competitive and crucial for reliable future assessments.
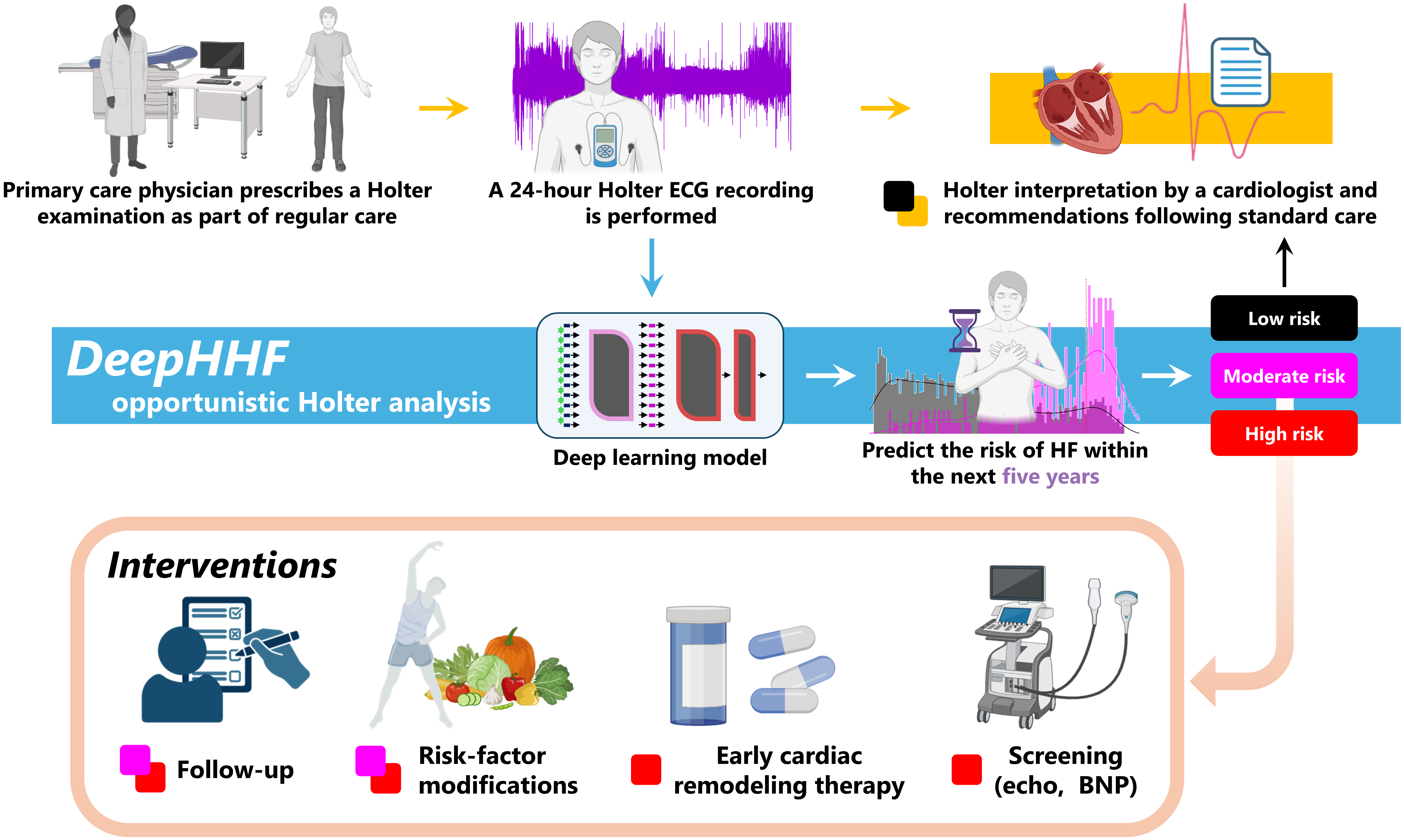
A new deep learning model analyzes full-day electrocardiograms to forecast heart failure risk up to five years before traditional diagnosis.