Beyond FLOPs: Governing the Next Wave of AI
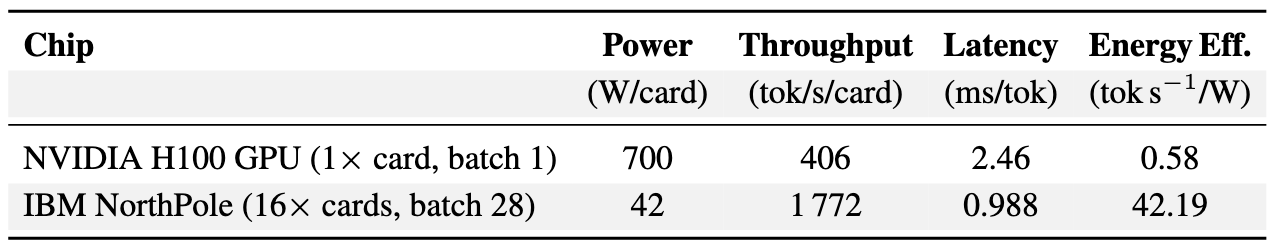
As artificial intelligence moves beyond conventional deep learning, current regulatory frameworks struggle to address the unique challenges posed by brain-inspired computing architectures.

As artificial intelligence moves beyond conventional deep learning, current regulatory frameworks struggle to address the unique challenges posed by brain-inspired computing architectures.
A new framework reveals how the spectral properties of key network operators govern both the robustness and interpretability of deep learning models.
![The pipeline rigorously analyzes post-event data, establishing a framework for quantifying performance metrics and iteratively refining the underlying algorithms to ensure mathematical correctness and provable outcomes [latex] \forall \epsilon > 0 [/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.01798v1/pipeline.png)
This research details a new science gateway that streamlines post-disaster analysis by combining photogrammetry and machine learning techniques.
![The SpecTF framework encodes both time series data and textual information into the frequency domain, then integrates them via a Frequency Cross-Modality Fusion-employing attention mechanisms and complex multiplication [latex] \odot [/latex]-to map historical frequency representations into predictive ones, ultimately projecting these back into the temporal domain for forecasting.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.01588v1/x1.png)
Researchers have developed a novel method for integrating textual information with time series data to improve the accuracy of future predictions.
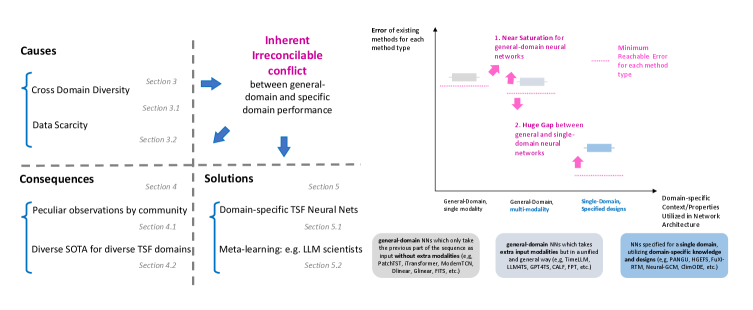
A new perspective argues that the pursuit of a single, all-powerful time series forecasting model is fundamentally limited, necessitating a move towards adaptable and domain-specific approaches.
![The study draws a parallel between the complexities of human societal structures and the emerging dynamics of agentic AI systems, proposing a four-component ([latex]4C[/latex]) mapping to understand how these artificial societies might evolve and interact.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.01942v1/x3.png)
As artificial intelligence becomes more autonomous, securing these systems requires moving beyond traditional defenses and focusing on the behavior and governance of AI agents within complex social environments.
A new approach to Bitcoin price prediction leverages the combined strengths of multiple machine learning models to achieve significantly improved accuracy.
Researchers are integrating advanced mathematical tools with machine learning to forecast critical transitions in complex systems before they occur.
![The study demonstrates an inherent tension in financial artificial intelligence, revealing that increased model accuracy frequently correlates with diminished interpretability-a phenomenon where the complexity required for higher predictive power compromises the ability to understand the reasoning behind those predictions, effectively establishing an accuracy-explainability frontier that limits simultaneously optimizing both qualities, much like the principle expressed by [latex] \Delta x \Delta p \geq \frac{\hbar}{2} [/latex] in quantum mechanics.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.01368v1/x1.png)
Deploying artificial intelligence in finance demands more than just predictive power, requiring a delicate balance between performance, regulation, and genuine understanding.
![The system architecture details a multi-agent approach to real estate investment trusts (REITs) trading, suggesting that even complex financial strategies are ultimately vulnerable to the unpredictable forces of a market mirroring humanity’s own self-deceptions - a system built on assumptions that, like light, can disappear beyond a point of no return [latex] \lim_{r \to \in fty} f(r) = 0 [/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.00082v1/diagram-en.png)
A novel multi-agent system powered by large language models is demonstrating promising results in the automated trading of Chinese public Real Estate Investment Trusts.