Beyond Outliers: Fast, Reliable Bayesian Inference with Simulations
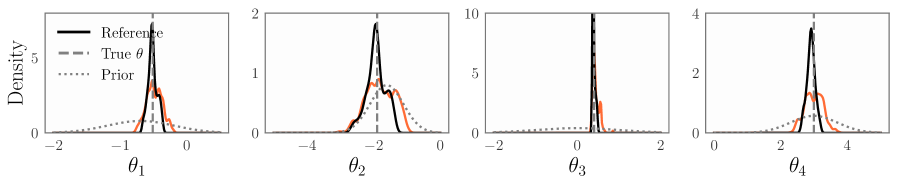
A new method, NSM-Bayes, dramatically improves the speed and robustness of Bayesian inference by leveraging neural networks and simulation.

A new method, NSM-Bayes, dramatically improves the speed and robustness of Bayesian inference by leveraging neural networks and simulation.
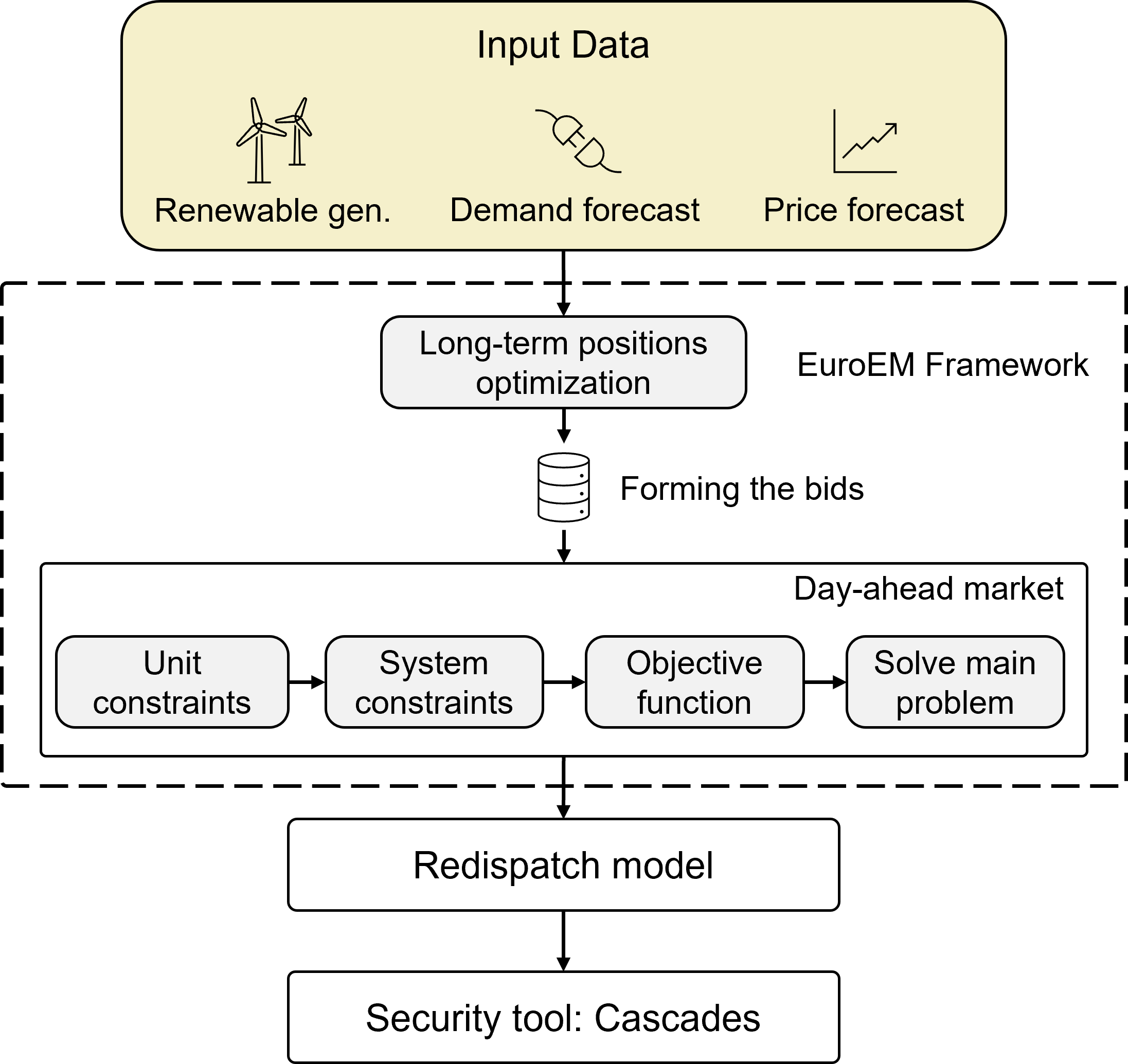
New research reveals that standard power grid security assessments often fail to account for how actual market behavior impacts system resilience.
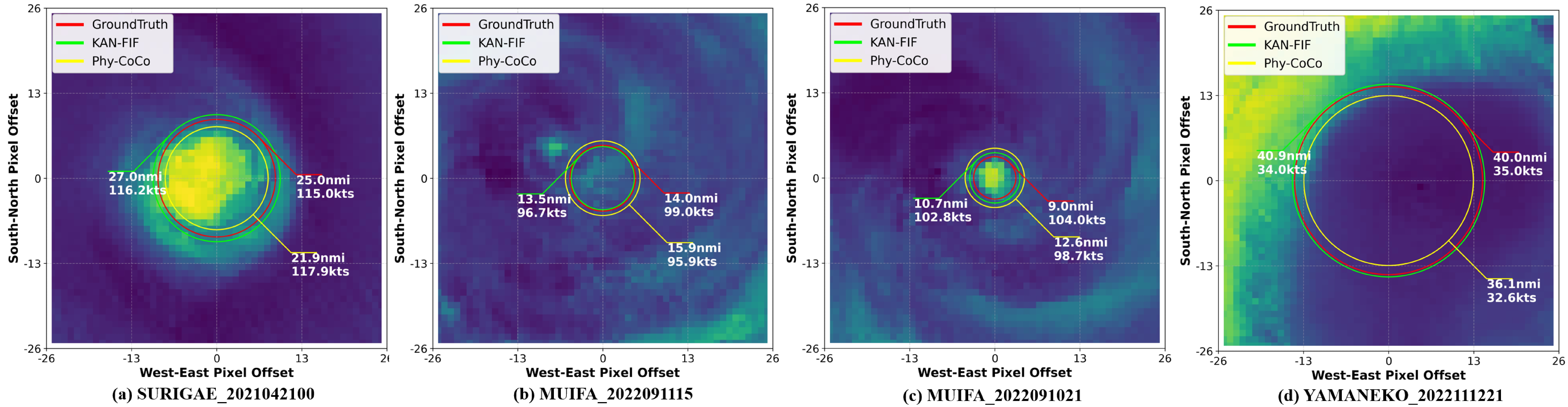
A new deep learning framework leverages satellite data and physics-informed machine learning to accurately and efficiently estimate tropical cyclone intensity and size.
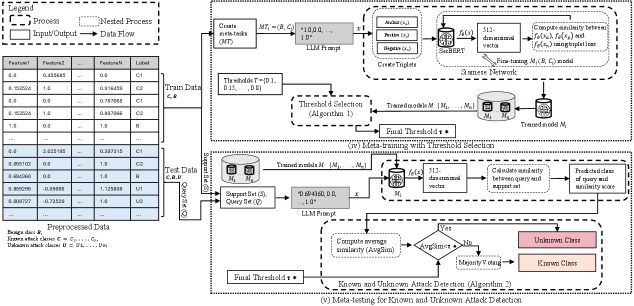
A new approach harnesses the power of language models and Siamese networks to identify previously unseen attacks targeting vulnerable IoT devices.
![The system exhibits distinct regimes of interpretational behavior-ambiguity, where interpretations diverge semantically yet yield consistent results ([latex] \mathbf{W}\_{RR} [/latex] high, [latex] \mathbf{W}\_{II} [/latex] off-diagonal low, resulting in high [latex] H_{I} [/latex], low [latex] H_{R|I} [/latex]), and instability, where similar interpretations produce widely varying results ([latex] \mathbf{W}\_{II} [/latex] off-diagonal high, [latex] \mathbf{W}\_{RR} [/latex] low, yielding low [latex] H_{I} [/latex], high [latex] H_{R|I} [/latex])-as evidenced by the relationships encoded within the system matrices [latex] \mathbf{W} [/latex] and the interpretation-result assignments [latex] \mathbf{W}\_{IR} [/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.12015v1/figure_1.png)
New research dissects the sources of error in large language models, separating genuine ambiguity from inherent instability to improve their reliability.
![Figure 1: Overview of AIR. The architecture anticipates inevitable decay, manifesting as a recursive loop where learned representations are continuously refined through iterative prediction - a process formalized as [latex] x_t = f(x_{t-1}) + \epsilon [/latex] - and subsequently distilled into a latent space, acknowledging that any attempt to impose rigid structure upon a dynamic system merely delays, rather than prevents, its eventual entropic unraveling.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.11749v1/x1.png)
As AI agents become more prevalent, ensuring their safe operation requires robust incident response mechanisms.
New research utilizes simulated patients to evaluate the trustworthiness of AI conversational agents tasked with recommending antidepressants.
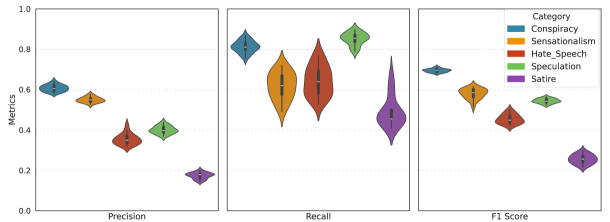
A large-scale study reveals that artificial intelligence can reliably identify harmful content related to U.S. elections with greater consistency than human reviewers.

New research reveals that self-improving artificial intelligence systems are fundamentally prone to losing their initial safety constraints over time.
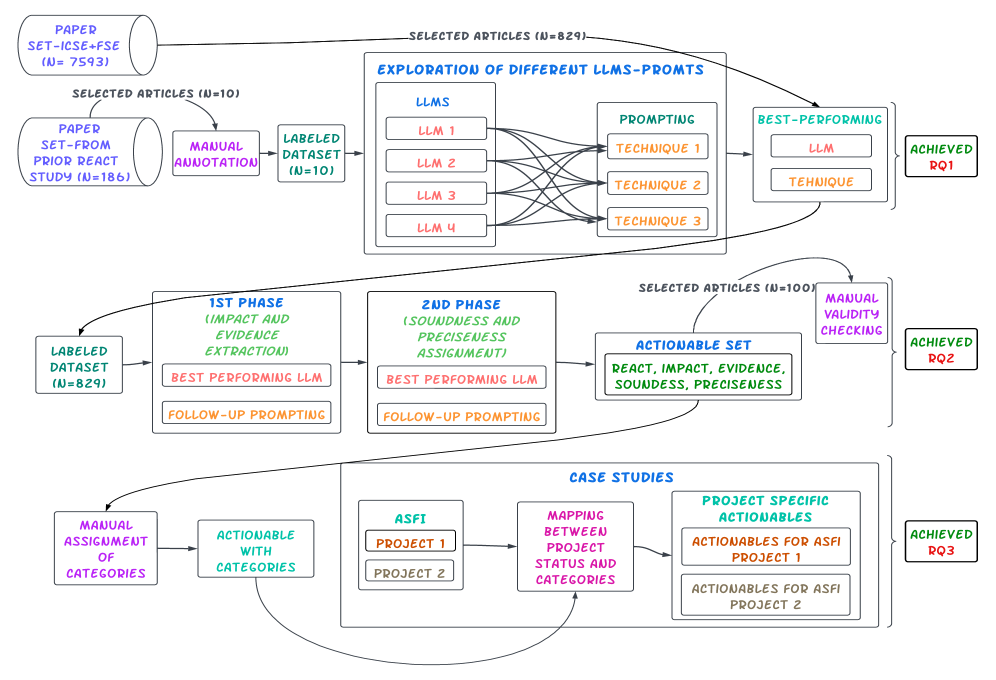
A new approach automatically extracts practical advice from academic studies to help open-source projects thrive.