Mining Research for Open Source Survival
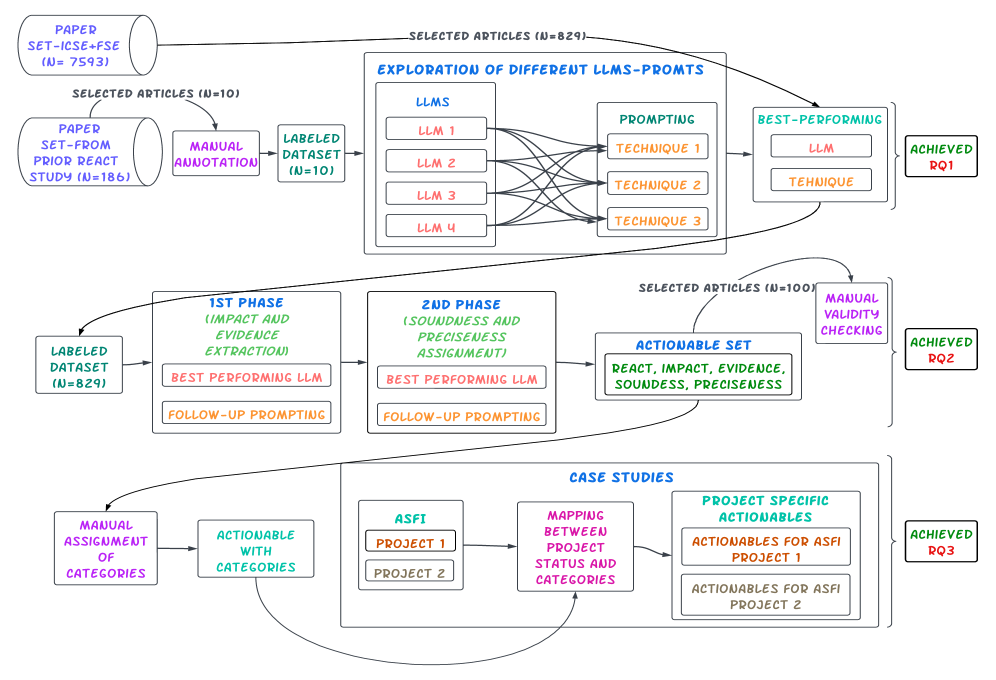
A new approach automatically extracts practical advice from academic studies to help open-source projects thrive.

A new approach automatically extracts practical advice from academic studies to help open-source projects thrive.
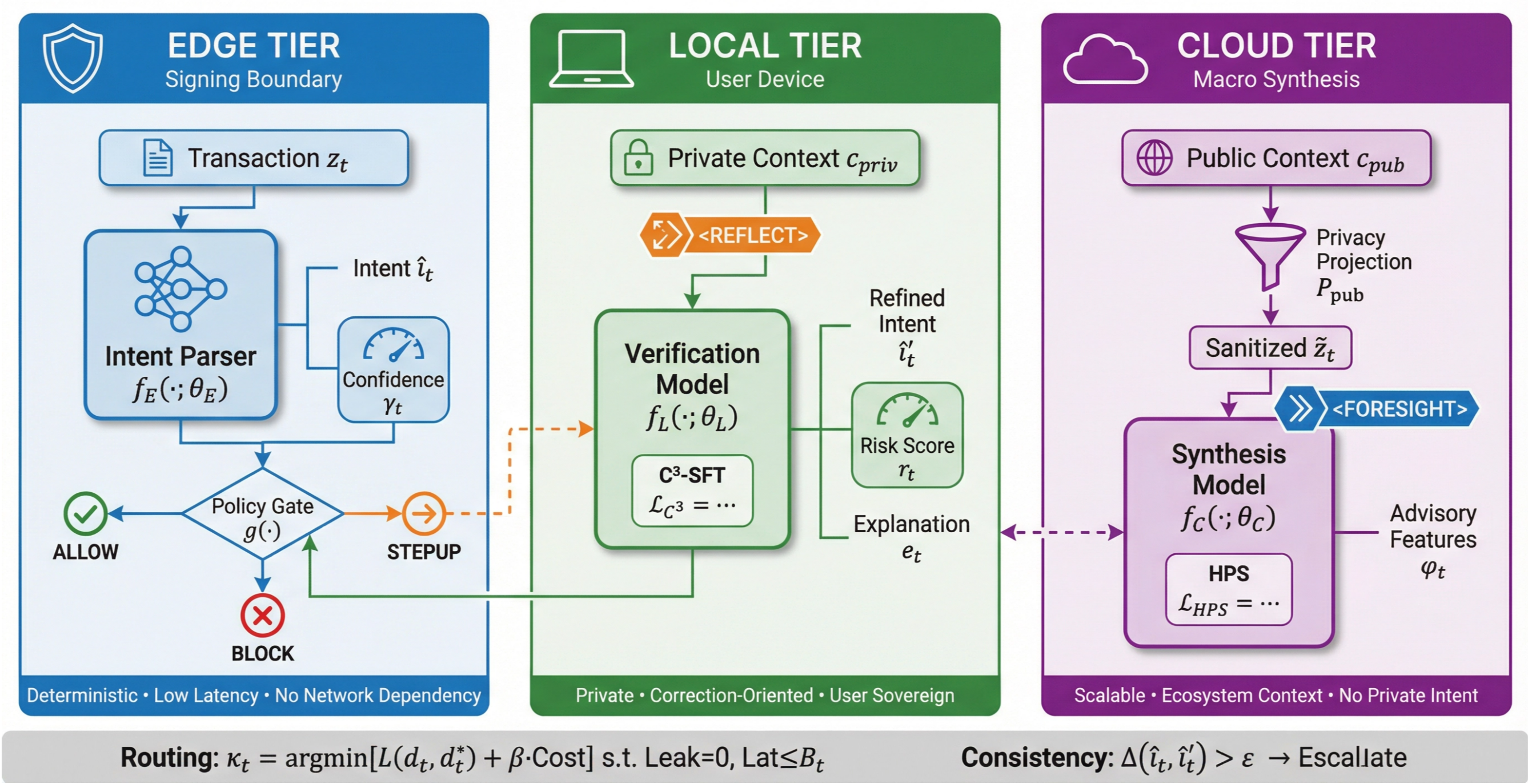
A new Edge-Local-Cloud architecture, DMind-3, promises safer, faster, and more private transaction execution by prioritizing user control and robust verification.
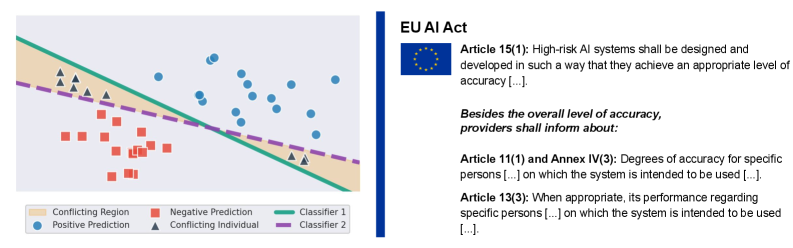
The EU AI Act aims to regulate high-risk systems, but accurately assessing individual performance becomes complex when multiple equally valid AI models offer differing predictions.

New research demonstrates a method for reducing unpredictable variations in clinical risk scores without compromising accuracy or transparency.
New research leverages machine learning and controlled experiments to forecast the onset of dangerous debris flows in burn scars, offering critical insights for mitigation efforts.
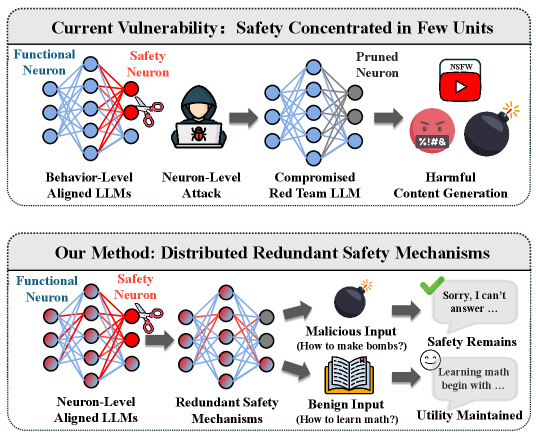
Researchers are exploring how to make large language models safer by directly intervening at the level of individual neurons.
![The system assesses agentic reasoning through trajectory-level uncertainty estimation, quantifying risk at each step by combining content-aware surprisal, repetition detection, action-observation mismatch, and user-agent coordination gaps-calculated as [latex]r\_{t}=\max(U\_{t},\alpha D\_{a}(t),\beta D\_{o}^{A}(t),\gamma D\_{o}^{U}(t))[/latex]-and then aggregates these risks using tail-focused metrics like top-K mean and the [latex]\ell\_{\in fty}[/latex] norm to identify potential failures in multi-turn interactions.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.11409v1/figures/overview.png)
New research introduces a method for assessing the risk of multi-step AI reasoning, moving beyond simple token-level probabilities to evaluate entire decision pathways.
A new framework explores how interconnected digital networks can overcome fragmentation and foster cooperation in an increasingly divided world.
A new architecture proposes shifting cybersecurity from reactive pipelines to proactive, self-governing AI agents that can adapt to evolving threats.
A new study assesses the performance of a hybrid machine learning-physics model in replicating key atmospheric phenomena and its limitations under extreme warming.