Listening for Trouble: AI-Powered Fault Detection in 3D Printers
A new approach uses sound and machine learning to identify mechanical failures in 3D printers as they happen.
A new approach uses sound and machine learning to identify mechanical failures in 3D printers as they happen.
A new agent-based model assesses the macroeconomic and distributional consequences of the UK’s Seventh Carbon Budget, offering crucial insights for policymakers.
![Crane’s architecture establishes a unified framework for large language model (LLM) serving, integrating components for request handling, model management, and efficient resource allocation to optimize throughput and minimize latency, as formalized in [latex] T = \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} t_i [/latex], where <i>T</i> represents average latency and <i>t<sub>i</sub></i> denotes the processing time for each request.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.15360v1/x1.png)
A new neural sketch, Crane, efficiently distills the essential information from continuously evolving graph data, offering a significant leap forward in stream summarization.
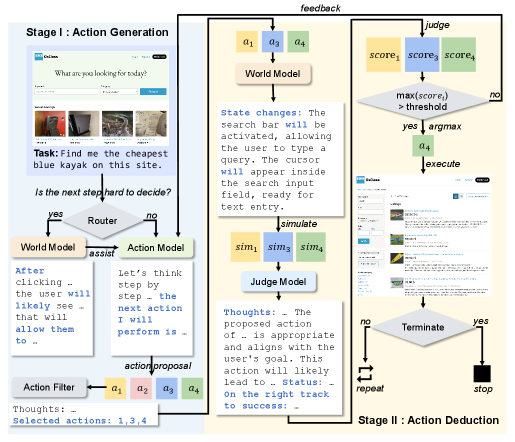
A new framework combines predictive modeling and reasoning to create web agents capable of anticipating errors and improving task completion in complex online environments.
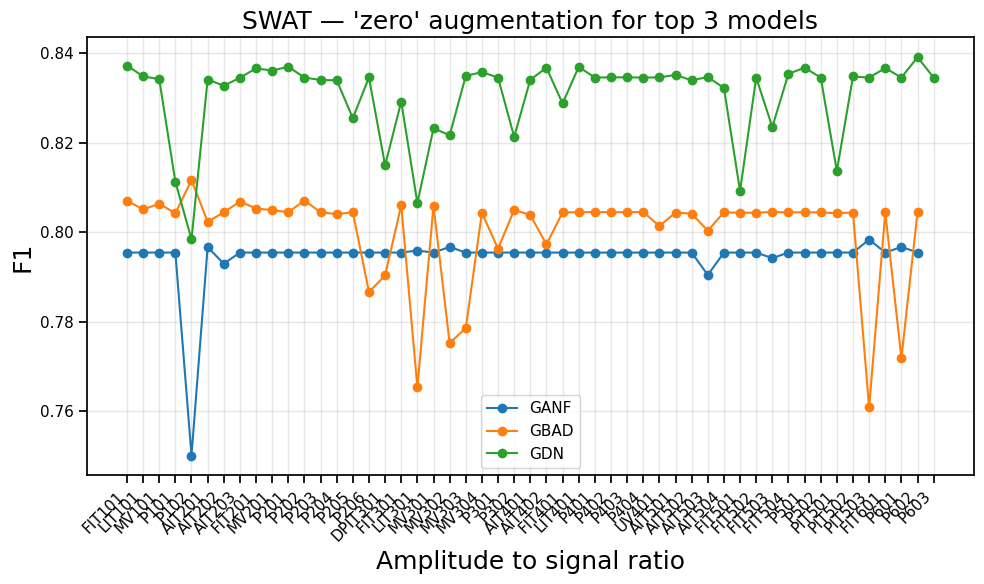
New research reveals that current anomaly detection models struggle with the complexities of real-world IoT deployments, necessitating a more rigorous and realistic benchmarking approach.
A new language model analyzes electrocardiograms to forecast cardiac events, offering a promising step toward proactive heart health management.
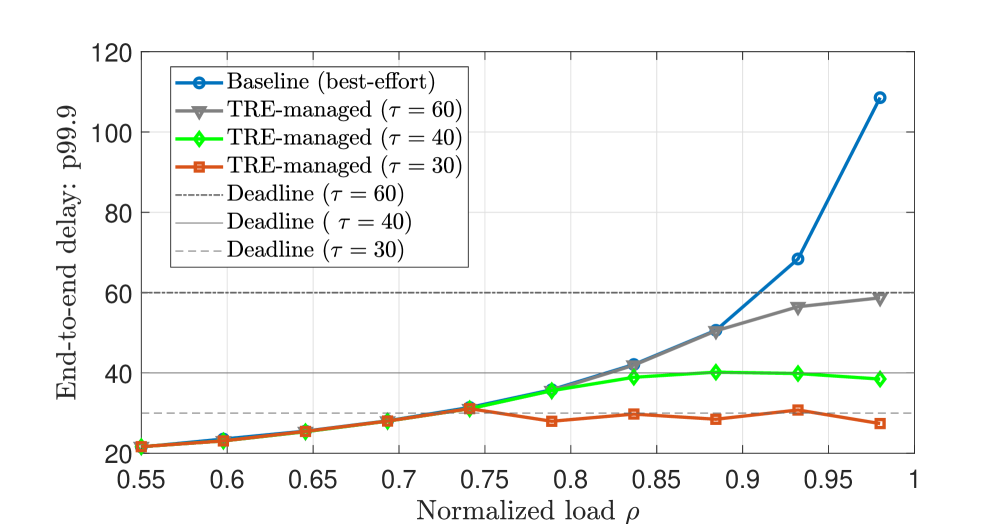
A new framework leverages composable contracts to guarantee performance and accountability across distributed AI services.
The convergence of agentic AI and advanced wireless networks promises enhanced security and privacy, but also introduces new vulnerabilities that demand careful consideration.
A structured approach to building and governing autonomous AI projects is essential for realizing their full potential and ensuring responsible development.
A review of medical data sharing, from the pioneering PhysioNet to today’s large foundation models, reveals both incredible promise and critical challenges for the future of AI in healthcare.