The AI Doomsdayscape: Why We Need to Question the Hype
A critical review unpacks the speculative narratives surrounding artificial intelligence and their often-overlooked ideological underpinnings.
A critical review unpacks the speculative narratives surrounding artificial intelligence and their often-overlooked ideological underpinnings.
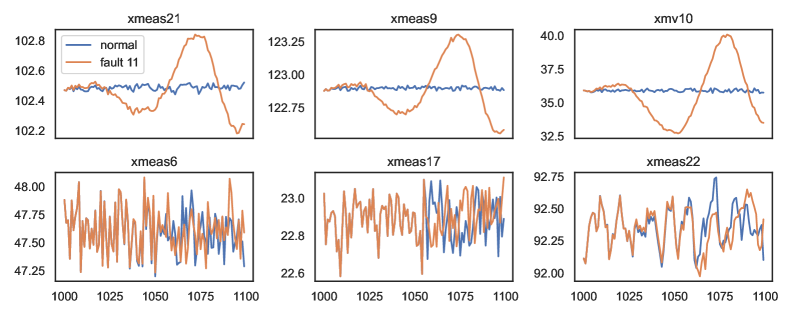
New research demonstrates how explainable AI techniques can illuminate the decision-making of deep learning models used to detect faults in complex chemical processes.
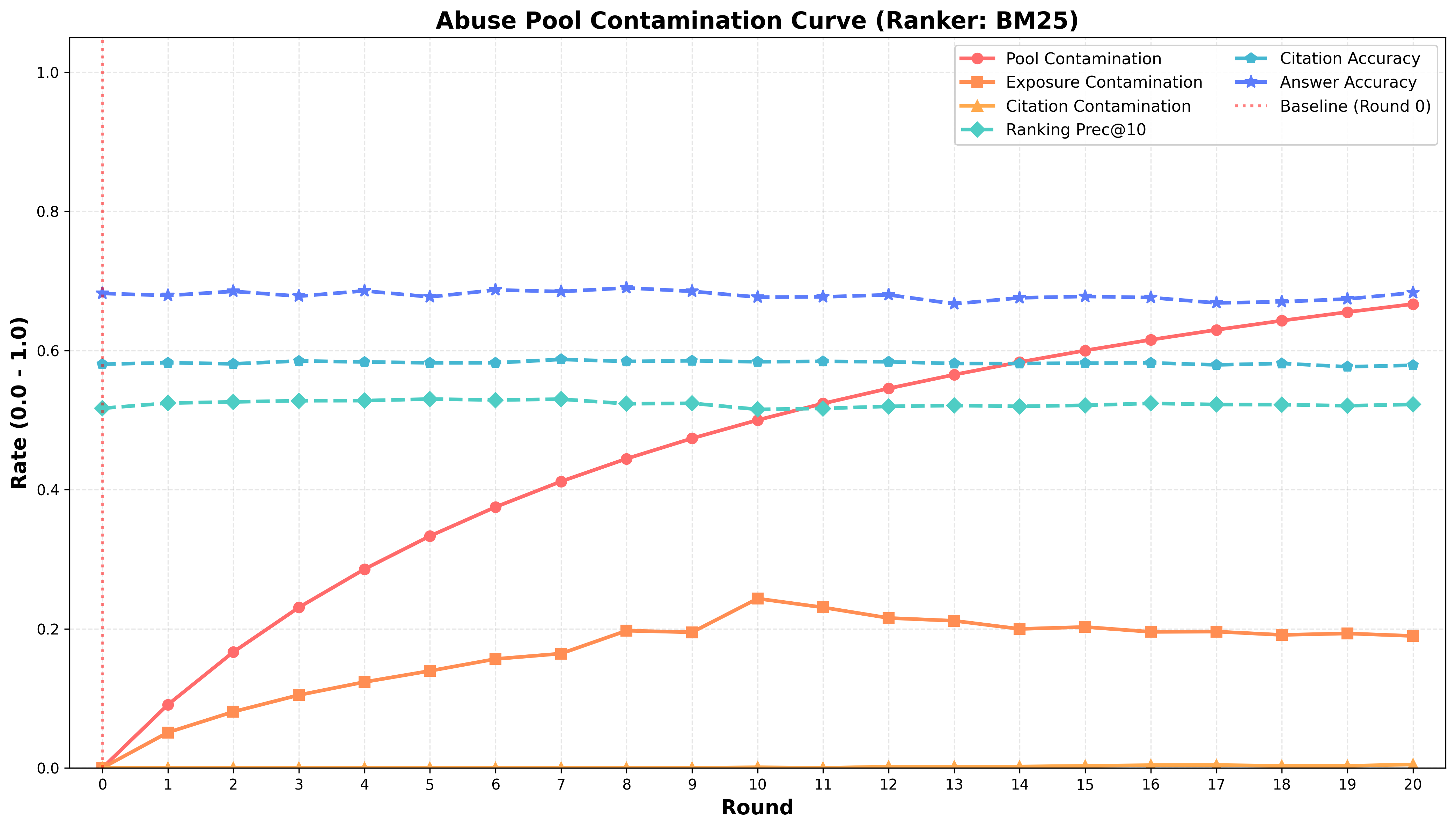
A new study reveals how the proliferation of AI-written content is quietly eroding the quality and diversity of online information retrieval.
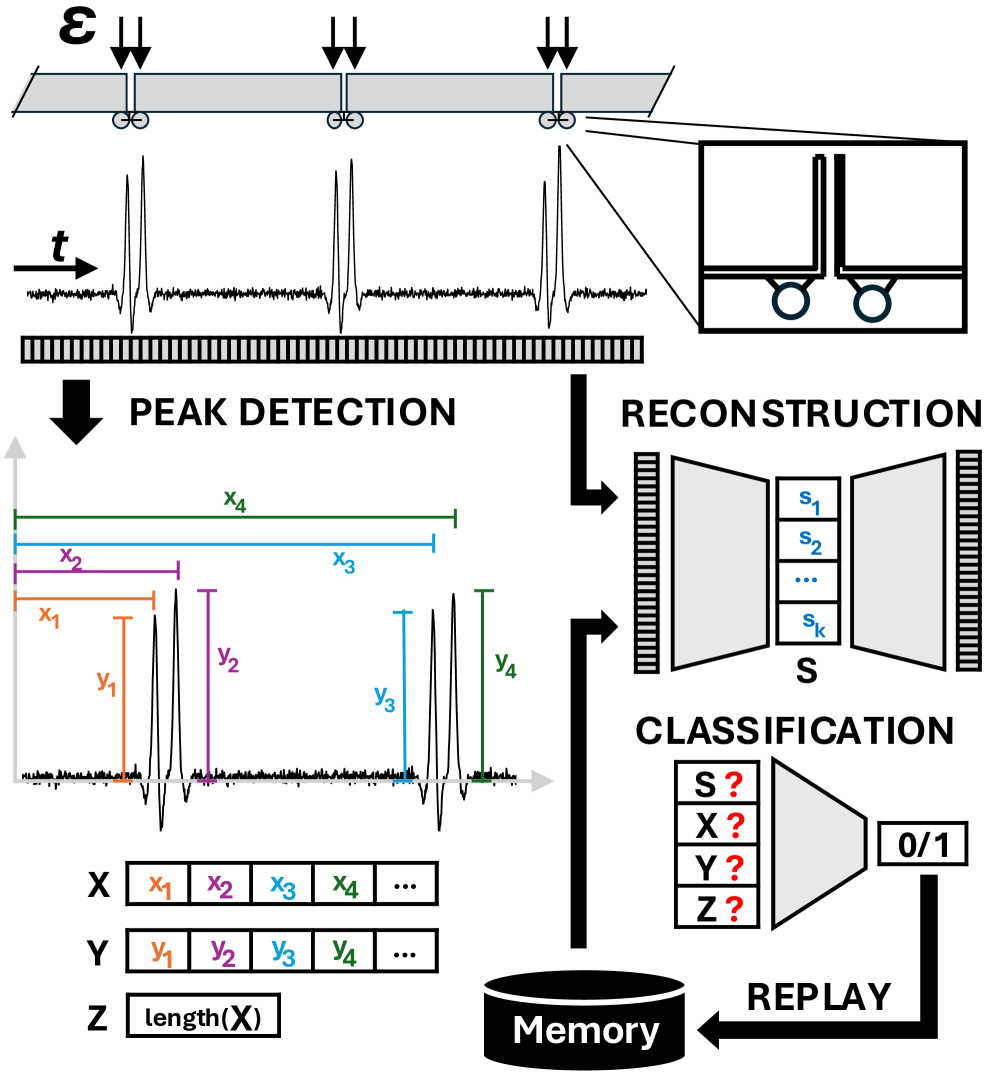
A new system uses sensor fusion and continual learning to predict and diagnose wheel defects in railway systems, enhancing safety and reducing maintenance costs.
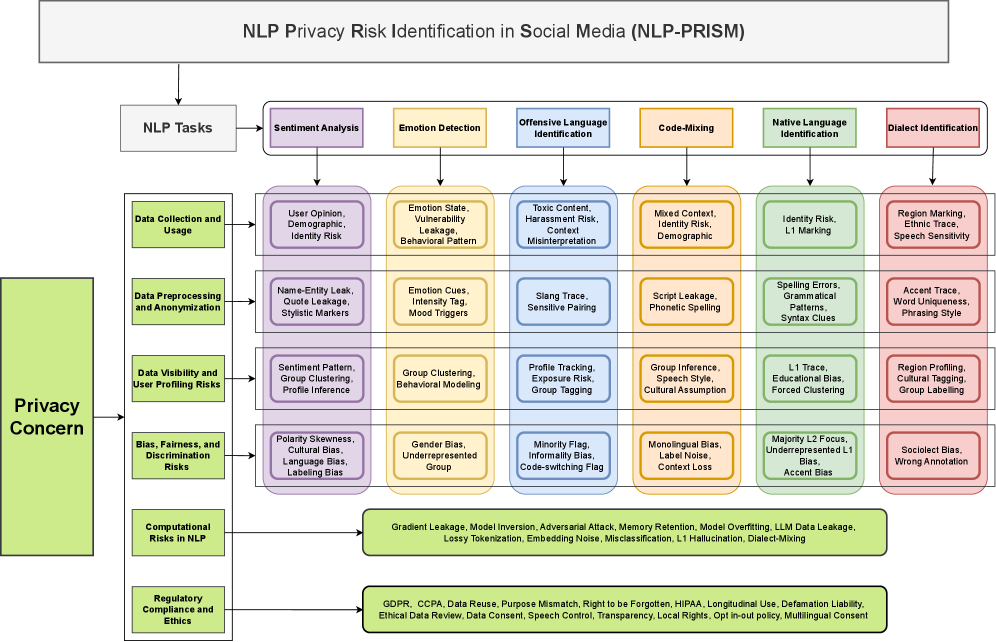
A new survey explores the growing vulnerabilities to personal data exposed by artificial intelligence systems used in social media platforms.
A new approach to fault detection uses fused sensor data and artificial intelligence to improve the reliability and efficiency of 3D printing processes.
A new machine learning approach leverages graph neural networks to simulate the complex dynamics of sea ice floes and improve predictions of their behavior.
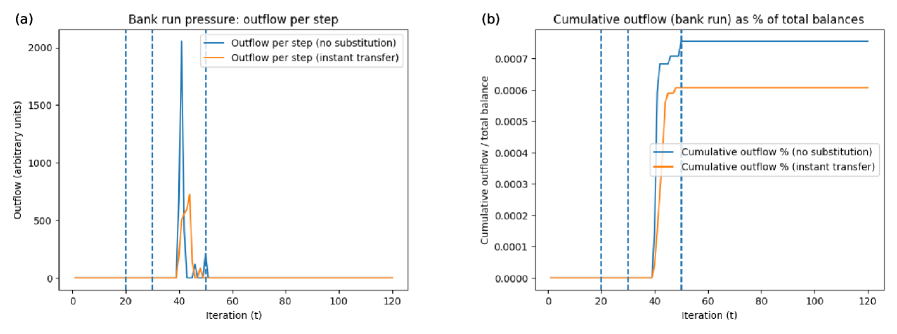
New research reveals that liquidity problems in payment networks can worsen after technical issues are resolved, driven by delayed behavioral shifts and persistent communication.
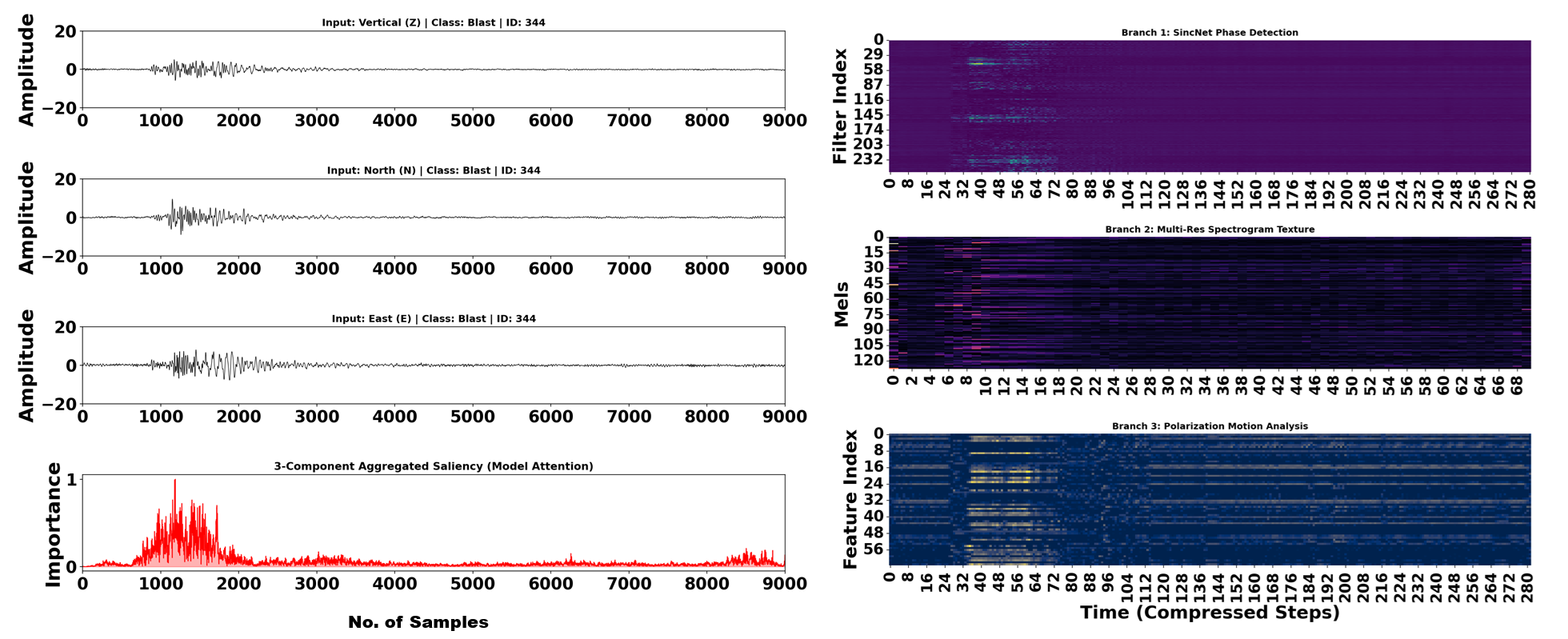
A new deep learning architecture combines seismological expertise with artificial intelligence to dramatically improve the accurate classification of seismic events.
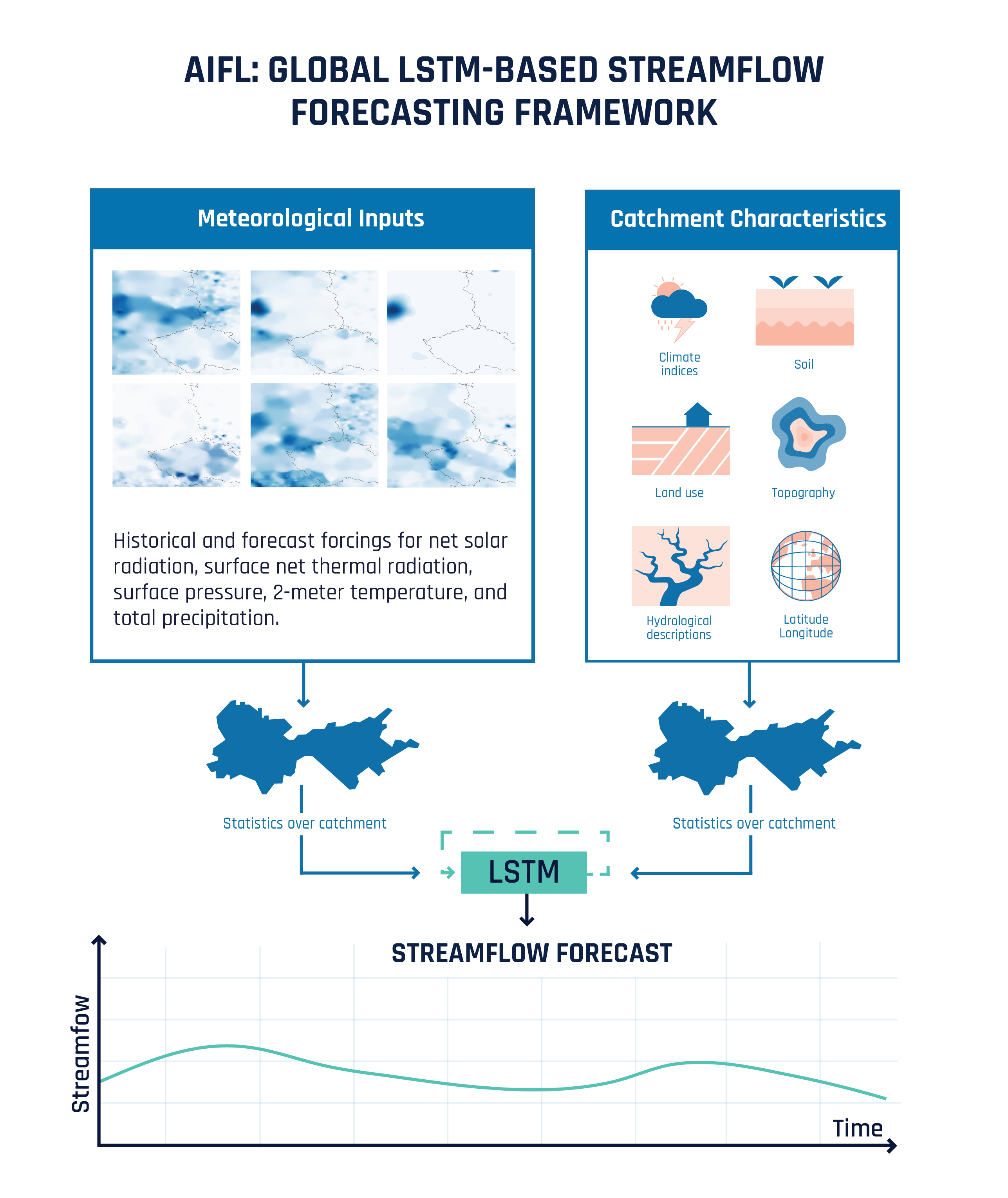
A new data-driven model, AIFL, delivers competitive streamflow predictions by leveraging the power of pre-trained machine learning and readily available weather data.