Beyond Correlation: A New Approach to Graph Classification
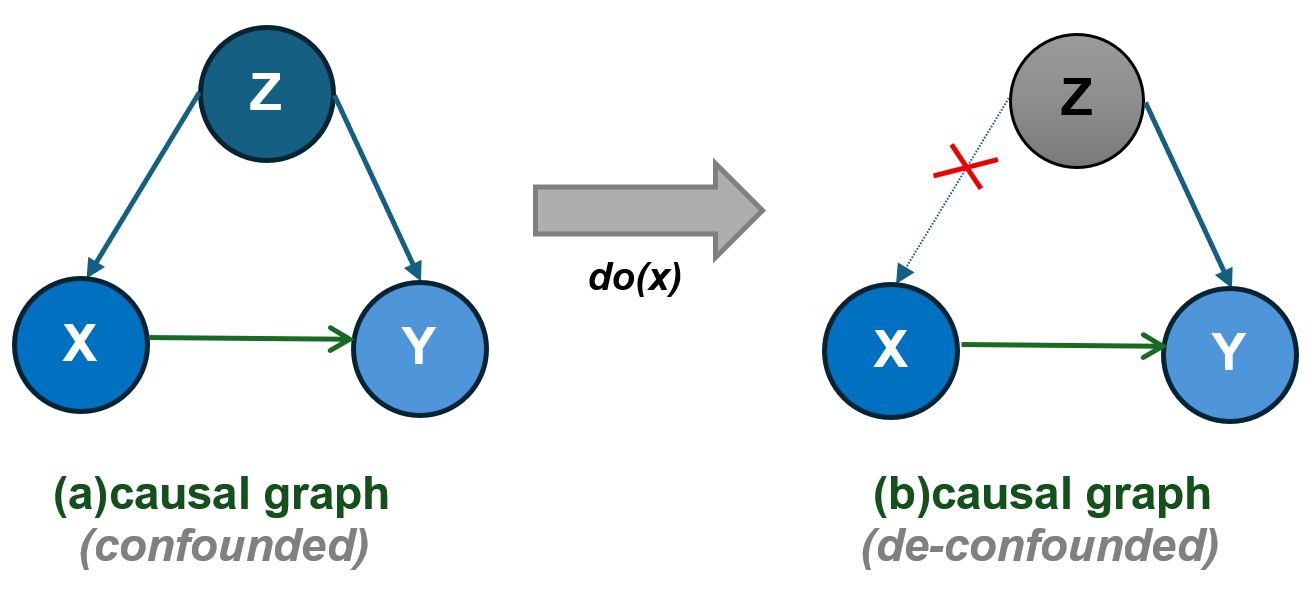
Researchers have developed a novel graph neural network that uses causal reasoning to improve accuracy and reliability in identifying key features within complex graph structures.

Researchers have developed a novel graph neural network that uses causal reasoning to improve accuracy and reliability in identifying key features within complex graph structures.
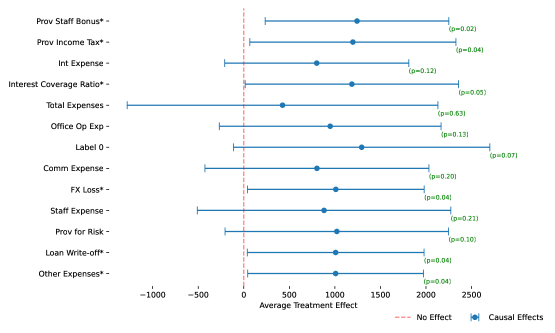
New research reveals a direct causal link between the language used in financial reports and a bank’s bottom line.
A new production-grade artificial intelligence system is providing national-scale weather forecasting and early warnings across South Africa, dramatically lowering the cost of disaster preparedness.
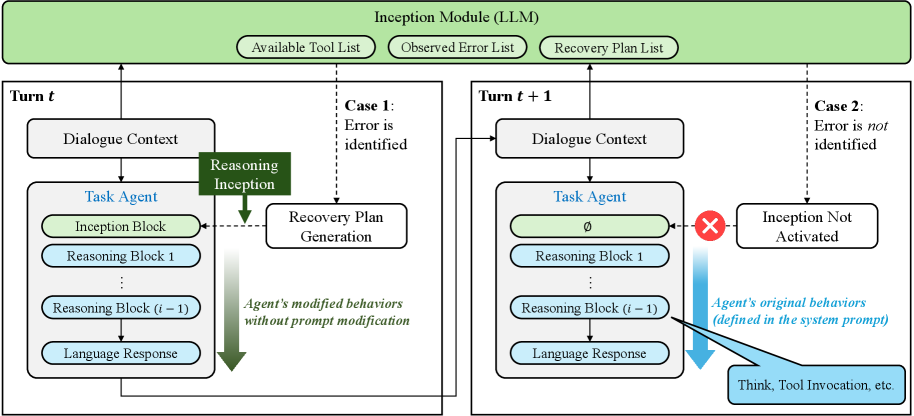
A new approach empowers conversational AI to identify and correct errors during complex, multi-turn interactions.
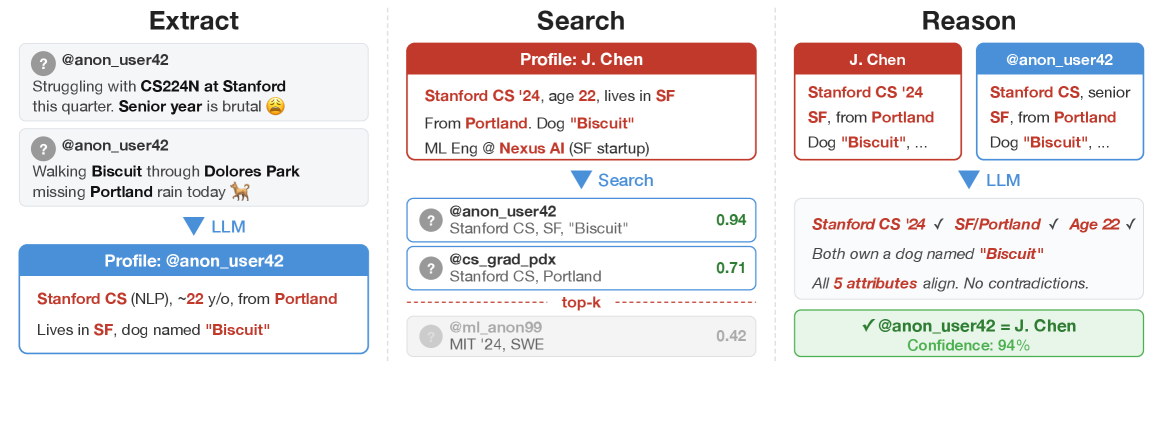
New research reveals that artificial intelligence can now automatically link pseudonymous online accounts to real-world identities with alarming accuracy.
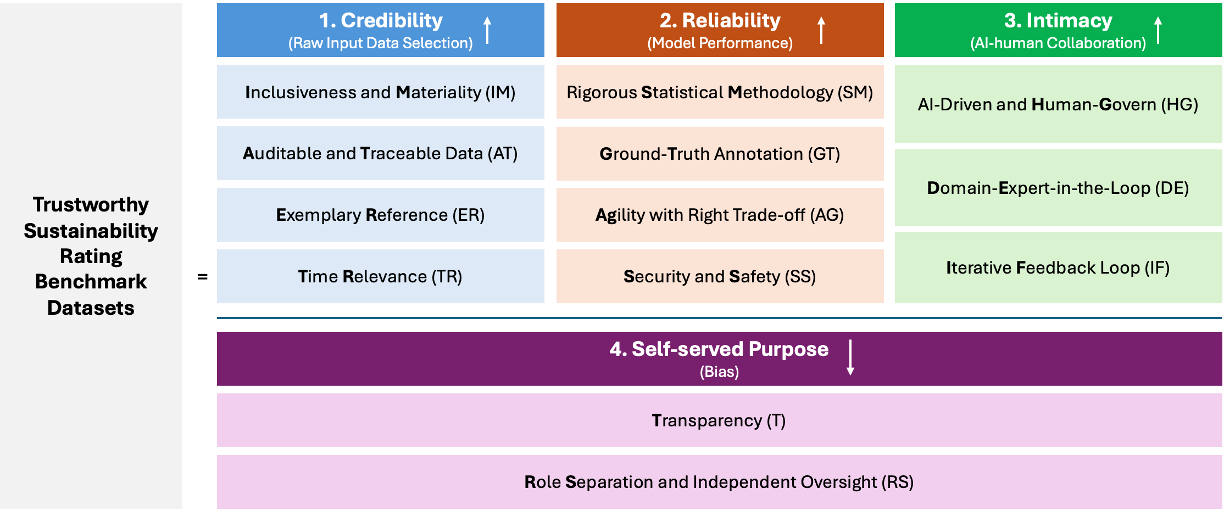
A new framework leverages the power of artificial intelligence and human expertise to assess the reliability of corporate sustainability ratings.
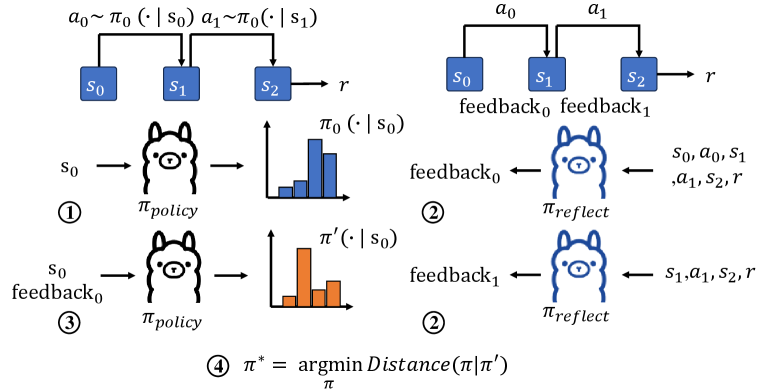
A new framework empowers artificial intelligence to learn more efficiently by retrospectively analyzing past experiences and assigning credit where it’s due.
![PaIRWaL encodes random walks on similarity networks derived from gyral folding to produce invariant sequences, subsequently aggregated to facilitate graph-level classification-a process fundamentally reliant on the topological properties of the underlying data and yielding representations insensitive to node permutations [latex] \mathbb{R}^n [/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17557v1/x1.png)
Researchers are leveraging the unique folding patterns of the brain to build more accurate diagnostic tools for Alzheimer’s and Lewy body dementia.
New research reveals how Bayesian algorithms like Thompson Sampling behave when faced with inaccurate models, offering insights into their robustness and potential pitfalls.
![The system’s state space trajectories, captured at intervals of approximately 10 seconds, demonstrate the predictive capacity of a Gaussian State Space model (red) and an autoencoder-LSTM network (green) against the backdrop of a periodically forced system (cyan) and its true response (black) as projected onto different phase space coordinates-specifically, [latex]x_{10}, \dot{x}_{10}, x_{11}[/latex] and [latex]x_1, \dot{x}_1, x_{20}[/latex]-revealing the models’ ability to approximate system behavior across varying states.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.16848v1/x16.png)
A new computational approach offers a faster and more precise method for determining the stable states of mechanical systems under unpredictable external influences.