Author: Denis Avetisyan
A novel multi-agent system powered by large language models is demonstrating promising results in the automated trading of Chinese public Real Estate Investment Trusts.
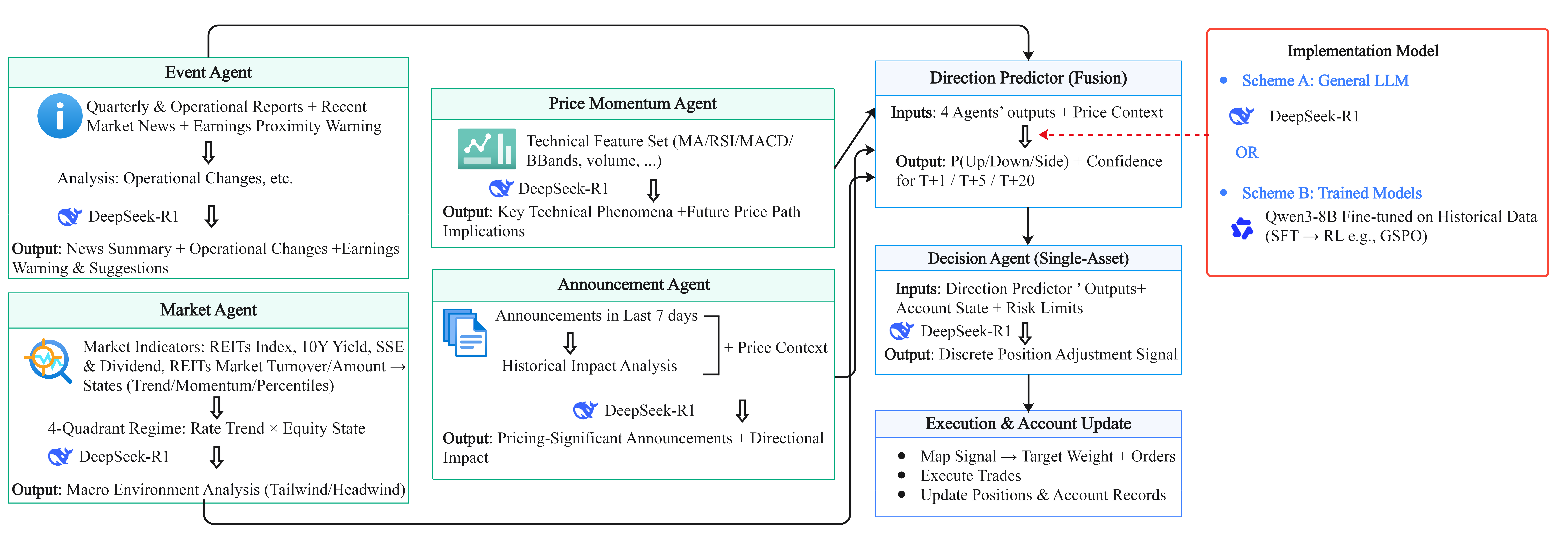
This paper details the design and empirical validation of an LLM-driven multi-agent system for trading Chinese Public REITs, showcasing improved risk-adjusted returns compared to a traditional buy-and-hold strategy.
While efficient market hypotheses suggest consistently outperforming benchmarks is challenging, this paper-‘Design and Empirical Study of a Large Language Model-Based Multi-Agent Investment System for Chinese Public REITs’-investigates a novel approach to quantitative trading utilizing multi-agent systems driven by large language models. The study demonstrates that this framework, incorporating agents for announcement analysis, event detection, price momentum, and market sentiment, significantly improves risk-adjusted returns compared to a buy-and-hold strategy in the Chinese Public REITs market. Notably, the research finds that fine-tuned small language models can achieve performance comparable to-or even exceeding-general-purpose large models within this system. Could this multi-agent, LLM-driven approach represent a scalable paradigm for navigating the complexities of modern financial markets and extracting alpha from diverse data sources?
The Illusion of Stability
Conventional trading strategies, predicated on substantial price fluctuations, frequently falter when applied to low-volatility markets such as Chinese Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). These REITs, characterized by limited price swings, present a distinct challenge to approaches reliant on capturing large, rapid movements. The typical buy-low, sell-high methodology yields diminished returns in such stable environments, necessitating a shift towards more sophisticated techniques. Instead of pursuing significant gains from pronounced price changes, successful navigation of this landscape requires identifying and exploiting subtle signals, capitalizing on minor shifts and incremental trends that would otherwise be overlooked. A nuanced approach, attuned to the specific dynamics of low-volatility assets, is therefore crucial for generating consistent returns.
The Chinese REITs market presents a distinct challenge to conventional trading strategies due to its persistently low volatility. Unlike markets characterized by significant price swings, extracting profit here necessitates a framework specifically attuned to subtle indicators. Traditional methods, reliant on large price movements, often fail to generate returns in such an environment. Consequently, successful navigation demands a sophisticated approach capable of deciphering nuanced patterns – minute shifts in trading volume, correlations between seemingly unrelated REITs, or even subtle changes in macroeconomic indicators – that would be lost in a more volatile setting. This framework isn’t about predicting large gains, but rather consistently capturing the value hidden within these minimal, yet meaningful, market signals.
The pursuit of profit within a low-volatility market necessitates a departure from conventional trading methodologies. When substantial price swings are infrequent, an adaptable framework becomes crucial, one designed to detect and leverage even the most subtle shifts in market dynamics. This doesn’t involve predicting large movements, but rather consistently capturing incremental gains from minor price adjustments. Such a framework often integrates high-frequency data analysis, sophisticated statistical modeling, and a keen sensitivity to factors that, in a more turbulent market, would be overshadowed by broader trends. Ultimately, success in this environment relies on a system’s ability to transform these seemingly insignificant movements into consistent, cumulative returns, highlighting the power of precision over prediction.
A Collective Intelligence for REITs
The MultiAgentFramework is designed to improve REIT investment performance by simulating a distributed intelligence system. This framework operates on the principle that aggregating insights from multiple specialized agents – each focused on a specific aspect of the real estate investment trust (REIT) market – yields more robust and accurate decision-making than a monolithic approach. The system’s architecture allows for parallel processing of market data and facilitates dynamic adjustments to investment strategies based on the collective output of its constituent agents, ultimately aiming to optimize risk-adjusted returns through diversified analysis and proactive response to market changes.
The multi-agent system utilizes specialized agents to comprehensively analyze real estate investment trust (REIT) markets from multiple perspectives. The PriceMomentumAgent identifies assets exhibiting sustained price increases or decreases, capitalizing on trend continuation. Simultaneously, the EventAgent monitors news feeds and regulatory filings to detect market-relevant occurrences – such as earnings releases or property acquisitions – that may impact asset valuations. Complementing these, the MarketAgent focuses on broader macroeconomic indicators and their influence on REIT performance, assessing factors like interest rates, inflation, and GDP growth to inform strategic asset allocation decisions.
The PredictionAgent within the multi-agent system utilizes historical price data and technical indicators to generate short-term price forecasts for REITs. These forecasts are probabilistic, providing a confidence interval alongside the predicted price movement. The DecisionAgent receives these forecasts, along with associated risk assessments, and converts them into actionable trading signals-specifically, buy, sell, or hold recommendations-based on pre-defined risk tolerance parameters and portfolio constraints. The output of the DecisionAgent includes the recommended trade volume and the target price, facilitating automated execution within the REIT portfolio.
Decoding Price with Language
The PredictionAgent utilizes the Qwen38B language model, a comparatively smaller-scale model with 38 billion parameters, specifically adapted for forecasting the direction of price fluctuations. This model was selected to balance predictive capability with computational efficiency, enabling real-time analysis and integration within the agent’s decision-making process. The directional price movement prediction task involves classifying potential price changes as either increasing or decreasing, outputting a prediction based on input market data. The smaller scale of Qwen38B, relative to larger models, allows for faster inference times and reduced resource consumption during operation.
The model alignment process incorporates both SupervisedFineTuning (SFT) and ReinforcementLearning (RL) methodologies. SFT initially trains the language model on a labeled dataset of historical market data, teaching it to predict price movements based on past performance. Subsequently, ReinforcementLearning is employed to further refine the model’s behavior, rewarding predictions that align with predefined trading objectives – such as maximizing profit or minimizing risk – and penalizing those that do not. This iterative process of SFT and RL ensures the model’s outputs are not only accurate based on historical data, but also strategically aligned with specific financial goals, optimizing it for practical trading applications.
The DeepSeekR1 model serves as the pre-trained base for the Qwen38B, providing a significant advantage in pattern recognition within financial market data. DeepSeekR1 underwent extensive training on a large corpus of text and code, enabling it to develop a strong understanding of sequential data and complex relationships. This pre-training process equips Qwen38B with initial weights and biases that are already attuned to identifying relevant features and dependencies, reducing the amount of task-specific training required for accurate price movement prediction and improving generalization performance on unseen market conditions. The robust pre-training effectively initializes the model, allowing it to more efficiently learn the nuances of financial data during the fine-tuning stages.
The model generates predictions regarding price movements not as simple directional signals, but as probability distributions. This probabilistic output quantifies the model’s confidence in each potential outcome – whether the price will increase, decrease, or remain stable – providing a nuanced assessment beyond binary classification. These probabilities are then utilized within the trading strategy to assess risk and potential reward, enabling informed decision-making that accounts for the inherent uncertainty of financial markets. Specifically, the probabilities inform position sizing, stop-loss orders, and take-profit levels, all contributing to a risk-managed approach to trading.
Performance Beyond the Horizon
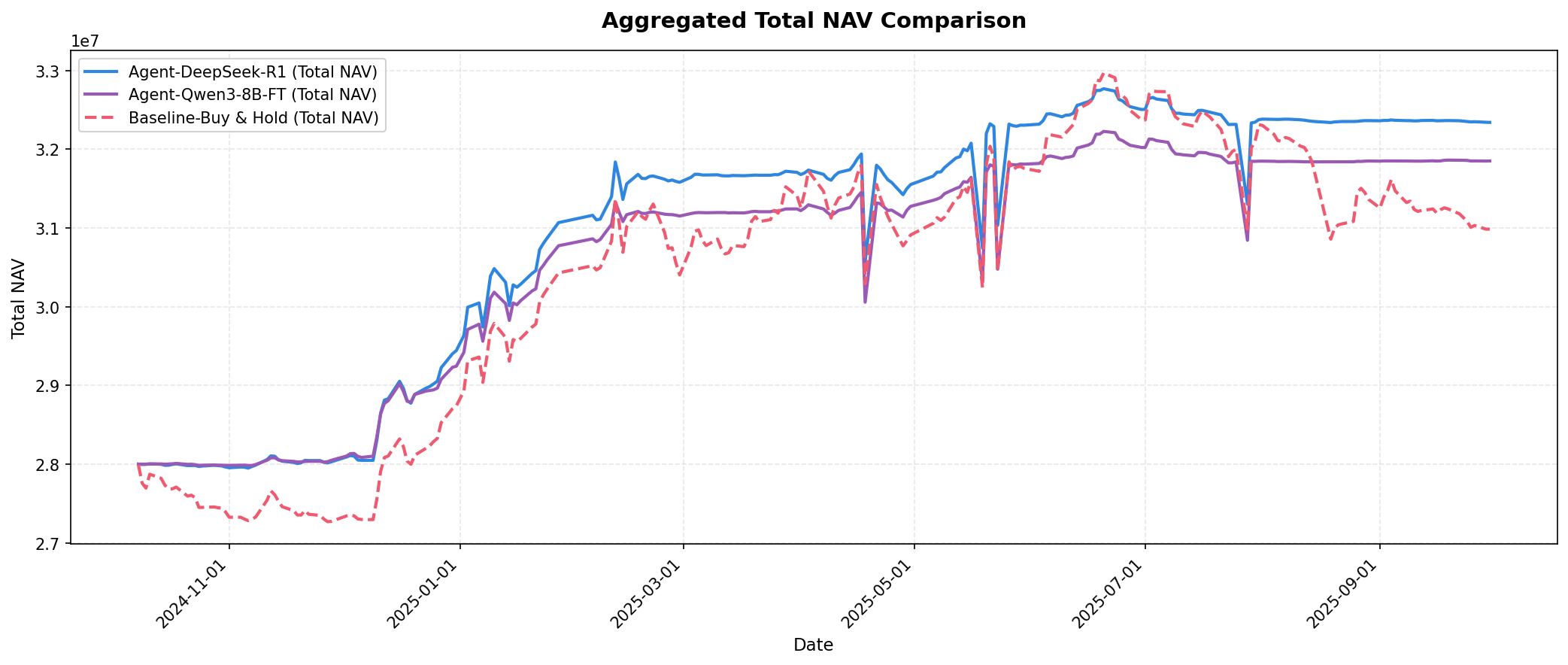
Rigorous backtesting of the MultiAgentFramework demonstrates a compelling capacity for generating positive returns. Across the evaluation period, the framework consistently outperformed a traditional Buy & Hold strategy, achieving a 15.50% CumulativeReturn when utilizing the DeepSeek-R1 agent and 13.75% with the Qwen3-8B-FT agent. This represents a significant improvement over the 10.69% return observed with the passive Buy & Hold benchmark, suggesting the framework’s multi-agent approach effectively identifies and capitalizes on market opportunities, translating into substantial gains for investors.
The MultiAgentFramework demonstrably outperforms a traditional Buy & Hold strategy not simply in raw returns, but in the efficiency with which those returns are generated, as evidenced by its significantly higher Sharpe Ratio. Values of 1.71, achieved with the DeepSeek-R1 agent, and 1.77 with Qwen3-8B-FT, stand in stark contrast to the 0.75 recorded by the Buy & Hold benchmark. This metric quantifies risk-adjusted return-essentially, the reward earned for each unit of risk taken-and a higher Sharpe Ratio indicates a superior ability to generate returns without incurring excessive volatility. The framework’s success in this regard suggests a sophisticated approach to portfolio management, skillfully balancing profit potential with downside protection and offering investors a more compelling risk-reward profile.
The MultiAgentFramework demonstrably strengthens portfolio protection during periods of market stress, as evidenced by significantly reduced maximum drawdown figures. Analysis reveals that the DeepSeek-R1 agent experienced a peak loss of only 4.09%, while the Qwen3-8B-FT agent limited losses to 3.46%. This contrasts sharply with the 11.12% maximum drawdown observed in a traditional Buy & Hold strategy, suggesting a substantially improved capacity to preserve capital during downturns. These findings indicate that the framework’s multi-agent approach effectively mitigates risk, delivering a more stable investment experience and bolstering long-term resilience compared to passive benchmarks.
The MultiAgentFramework demonstrably achieves its performance gains through a synergistic approach to market interaction. Rather than relying on a single predictive model, the system harnesses the diverse perspectives and strategies of multiple agents, effectively creating a collective intelligence. Backtesting indicates this distributed cognition translates into consistently positive returns, exceeding those of traditional buy-and-hold strategies. Importantly, the framework doesn’t simply chase gains; it actively manages risk, as evidenced by a significantly lower maximum drawdown and a substantially improved Sharpe ratio. This suggests the agents, through their interactions, collectively identify and mitigate potential downsides, resulting in a more stable and risk-aware investment profile – a testament to the power of decentralized decision-making in complex financial environments.
The research detailed within this paper posits a complex interplay between agent behavior and market response, mirroring the inherent limitations of predictive models. This echoes Stephen Hawking’s assertion: “Intelligence is the ability to adapt to any environment.” The multi-agent system, leveraging large language models, attempts precisely that – adaptation to the volatile landscape of Chinese Public REITs. However, as the study demonstrates, even sophisticated systems are bounded by the complexities of time series analysis and the unpredictable nature of financial markets. The pursuit of optimal returns, therefore, necessitates a continuous recalibration of strategies, acknowledging the ever-present horizon beyond which current understanding ceases to be reliable, much like the event horizon of a black hole.
What Lies Ahead?
The demonstrated capacity of large language models to navigate the complexities of Chinese Public REITs-to discern patterns within time series data and formulate trading strategies-is, at best, a local victory. The system’s performance, while exceeding a passive benchmark, serves as a poignant reminder that even sophisticated algorithms are predicated on historical data – a finite and inherently flawed representation of a dynamic market. Modeling requires careful consideration of not only market microstructure but also the inherent opacity of asset valuation and the unpredictable influence of external factors.
Future iterations must confront the limitations of current reinforcement learning paradigms. The pursuit of optimal strategies, while mathematically elegant, risks overfitting to the observed dataset and failing to generalize to unseen market conditions. The accretion disk of financial data exhibits anisotropic emission with spectral line variations, necessitating more robust methods for anomaly detection and risk assessment. A critical area of investigation lies in incorporating higher-order cognitive abilities into the agent architecture-the capacity for meta-learning, counterfactual reasoning, and the ability to question the very assumptions upon which its decisions are based.
Ultimately, the true test will not be the maximization of returns, but the system’s resilience in the face of unforeseen events-black swan occurrences that defy prediction and expose the fragility of even the most meticulously constructed models. The illusion of control is a persistent temptation; acknowledging the fundamental unknowability of the future is, paradoxically, the most prudent course.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.00082.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Lacari banned on Twitch & Kick after accidentally showing explicit files on notepad
- Adolescence’s Co-Creator Is Making A Lord Of The Flies Show. Everything We Know About The Book-To-Screen Adaptation
- YouTuber streams himself 24/7 in total isolation for an entire year
- The Batman 2 Villain Update Backs Up DC Movie Rumor
- Jane Austen Would Say: Bitcoin’s Turmoil-A Tale of HODL and Hysteria
- Now you can get Bobcat blueprint in ARC Raiders easily. Here’s what you have to do
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Dogecoin: Still Waiting for Liftoff 🚀
- Warframe Turns To A Very Unexpected Person To Explain Its Lore: Werner Herzog
- Jamie Lee Curtis & Emma Mackey Talk ‘Ella McCay’ in New Featurette
2026-02-03 11:39